Pinia
Pinia
Pinia 是 Vue 生态里 Vuex 的代替者,一个全新 Vue 的状态管理库, 是 Vue3 中推荐的状态管理库
Pinia 也是 Vuex 的开发团队开发的
特点
支持 Vue3 和 Vue2
完整的 TS 支持
足够轻量, 压缩后体积只有 1kb 左右
去除 mutations, 只有 state, getter, actions
actions 支持同步与异步
代码扁平化没有模板嵌套, 只有 store 的概念, store 之前可以自由使用, 每一个 store 都是独立的
无需手动添加 store, store 一旦创建会自动添加
安装
pnpm install pinia
引入注册 Vue3
main.ts:
import { createApp } from "vue";
import App from "./App.vue";
import { createPinia } from "pinia";
const store = createPinia();
let app = createApp(App);
app.use(store);
app.mount("#app");
使用
在 main.ts 中引入完 pinia 后就可以创建状态管理库了
再 src 目录下创建一个 store 文件夹, 在其中创建一个 index.ts 文件, 用于
- 定义状态管理库
- 修改容器中的
state - 仓库中
action的使用
示例:
@/store/store-names.ts:
export const enum Names {
TEST = "TEST",
}
@/store/index.ts
import { defineStore } from "pinia";
import { Names } from "./store-name";
export const useTestStore = defineStore(Names.TEST, {
// state 存储全局状态
state: () => {
return {
current: 1,
name: "233",
};
},
// computed like, 修饰一些值, 用于监视(计算)状态变化, 有缓存的功能
getters: {},
// methods, 可做同步异步, 提交state(用于修改 state 全局状态数据)
actions: {},
});
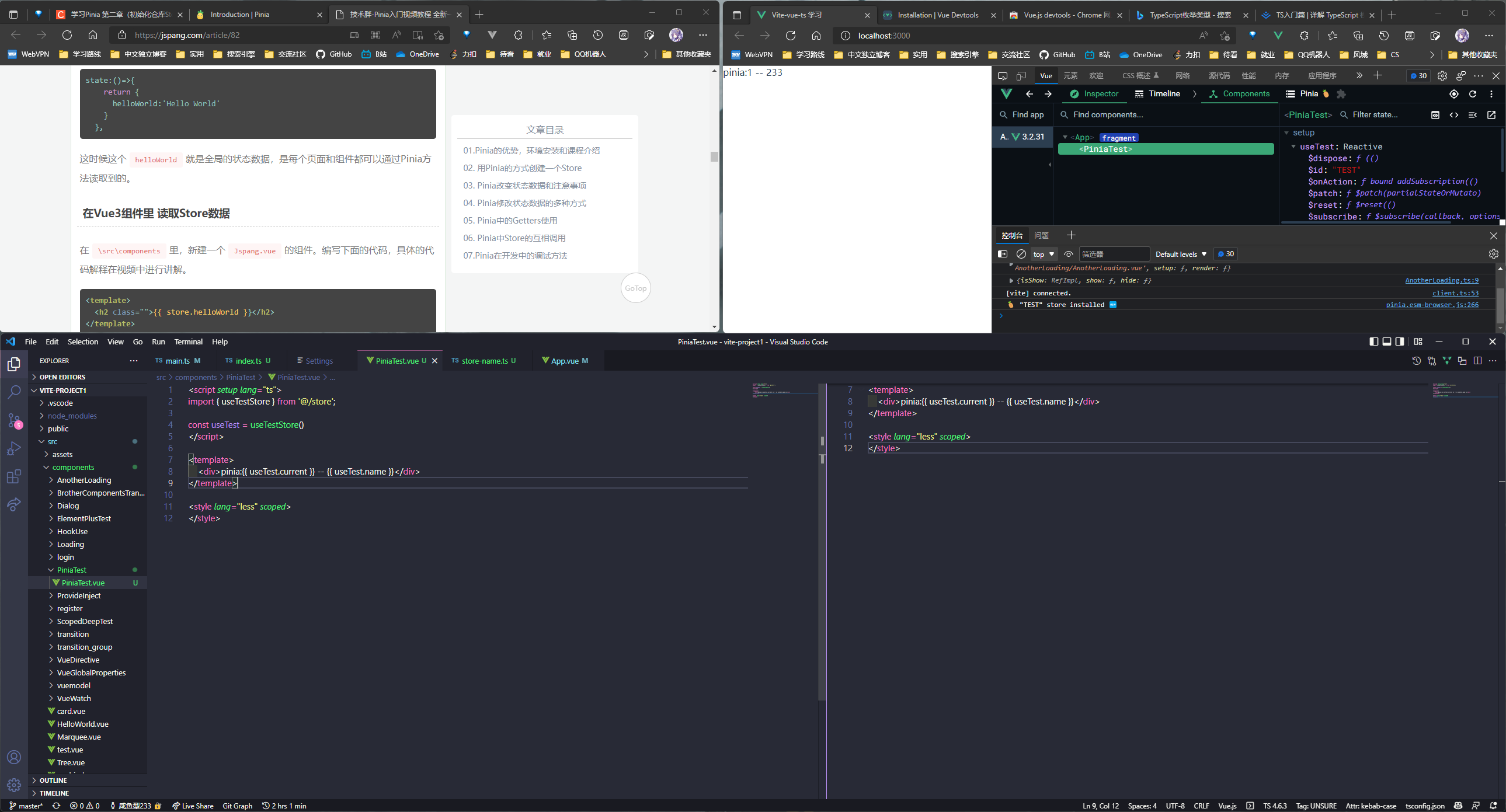
PiniaTest.vue:
<script setup lang="ts">
import { useTestStore } from "@/store";
const useTest = useTestStore();
</script>
<template>
<div>pinia:{{ useTest.current }} -- {{ useTest.name }}</div>
</template>
<style lang="less" scoped></style>
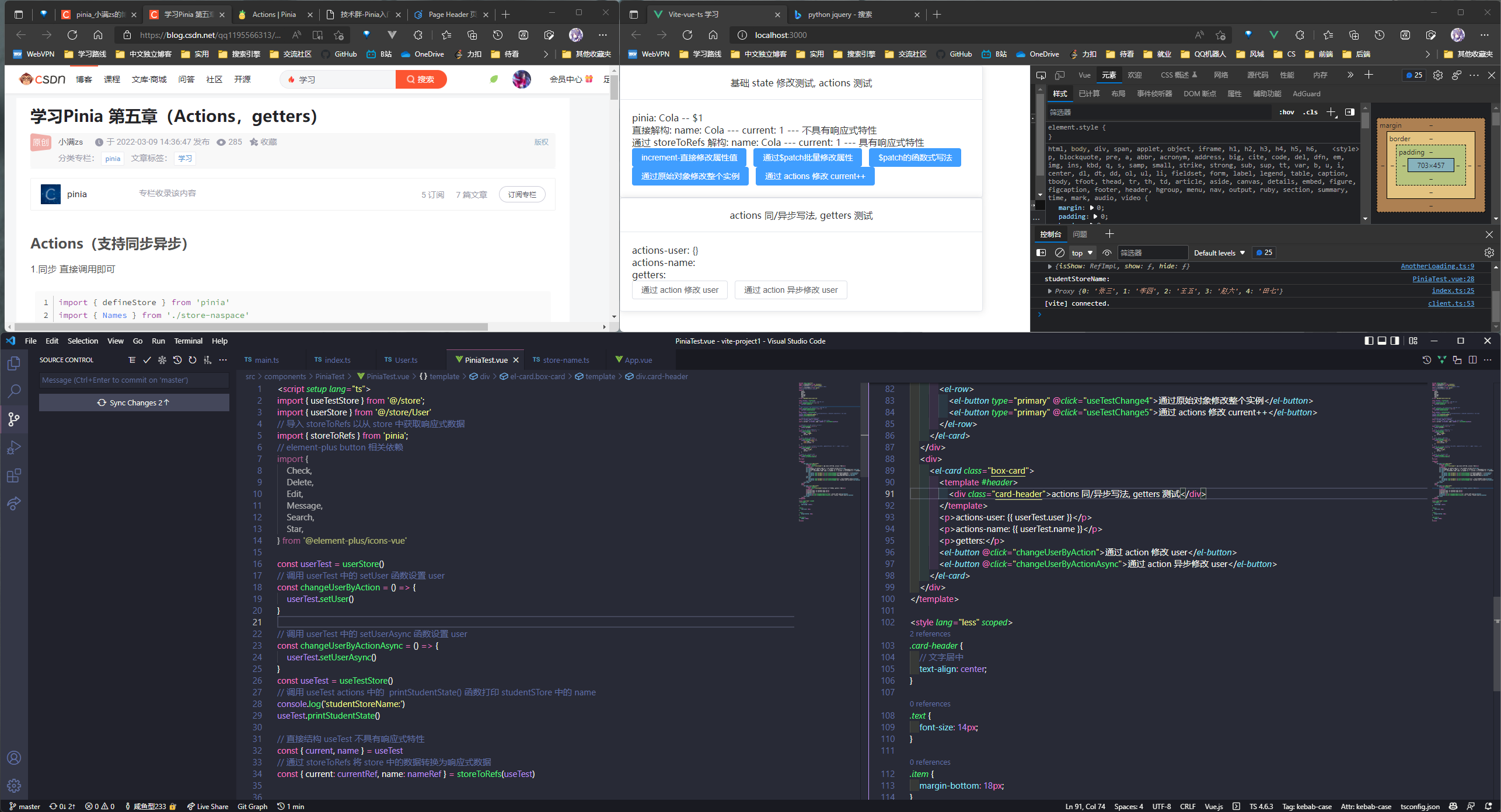
Pinia 状态修改
五种修改方式, 比 vuex 的写法要简洁, 具体示例如下:
@store/index.ts
import { defineStore } from "pinia";
import { Names } from "./store-name";
export const useTestStore = defineStore(Names.TEST, {
// state 存储全局状态
state: () => {
return {
current: 1,
name: "Cola",
};
},
// computed like, 修饰一些值, 用于监视(计算)状态变化, 有缓存的功能
getters: {},
// methods, 可做同步异步, 提交state(用于修改 state 全局状态数据)
actions: {
// current++
currentIncrement() {
this.current++;
},
},
});
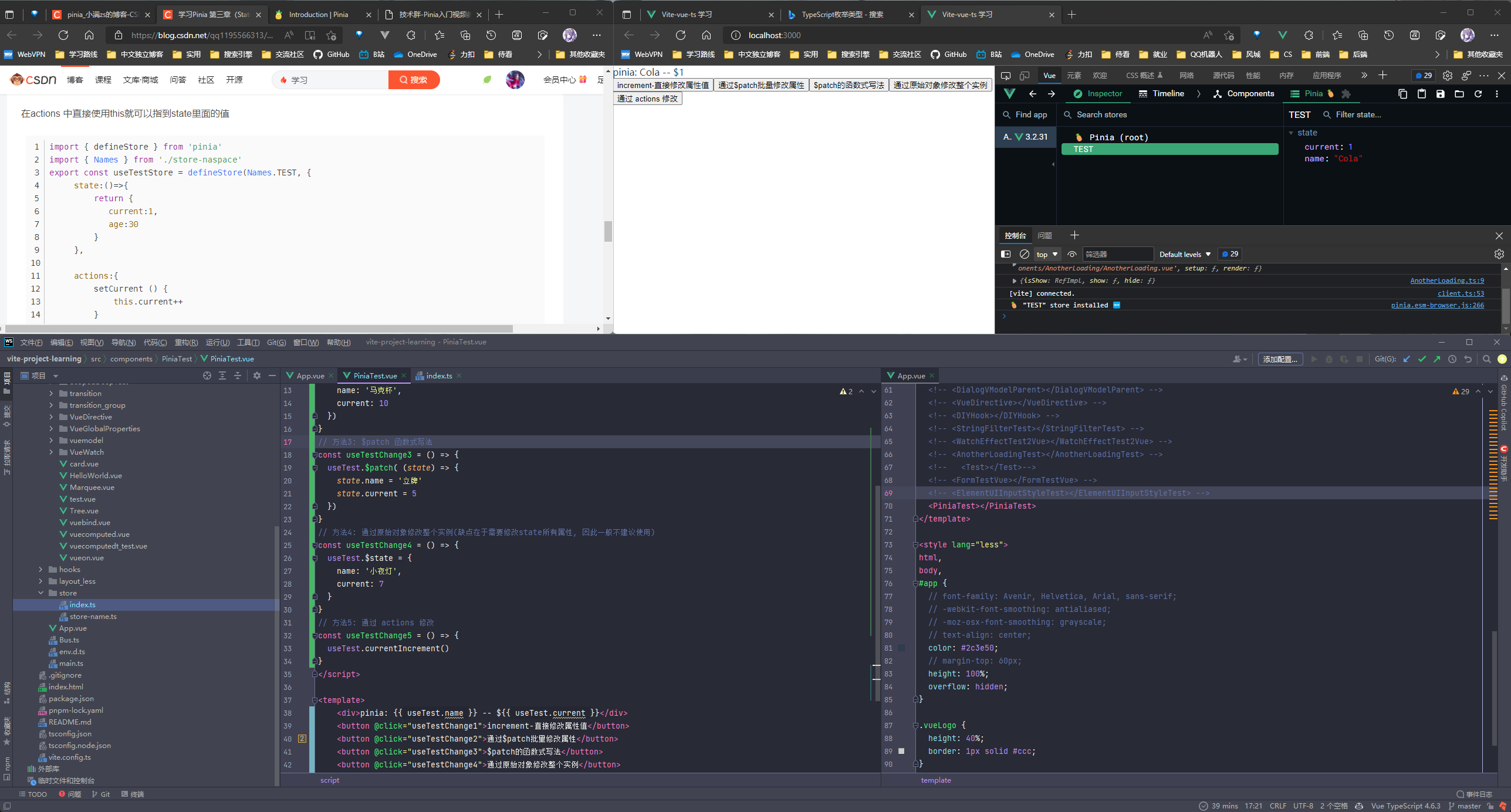
PiniaTest.vue
<script setup lang="ts">
import { useTestStore } from "@/store";
const useTest = useTestStore();
// 直接修改属性值实现 useTest.current++
const useTestChange1 = () => {
useTest.current++;
};
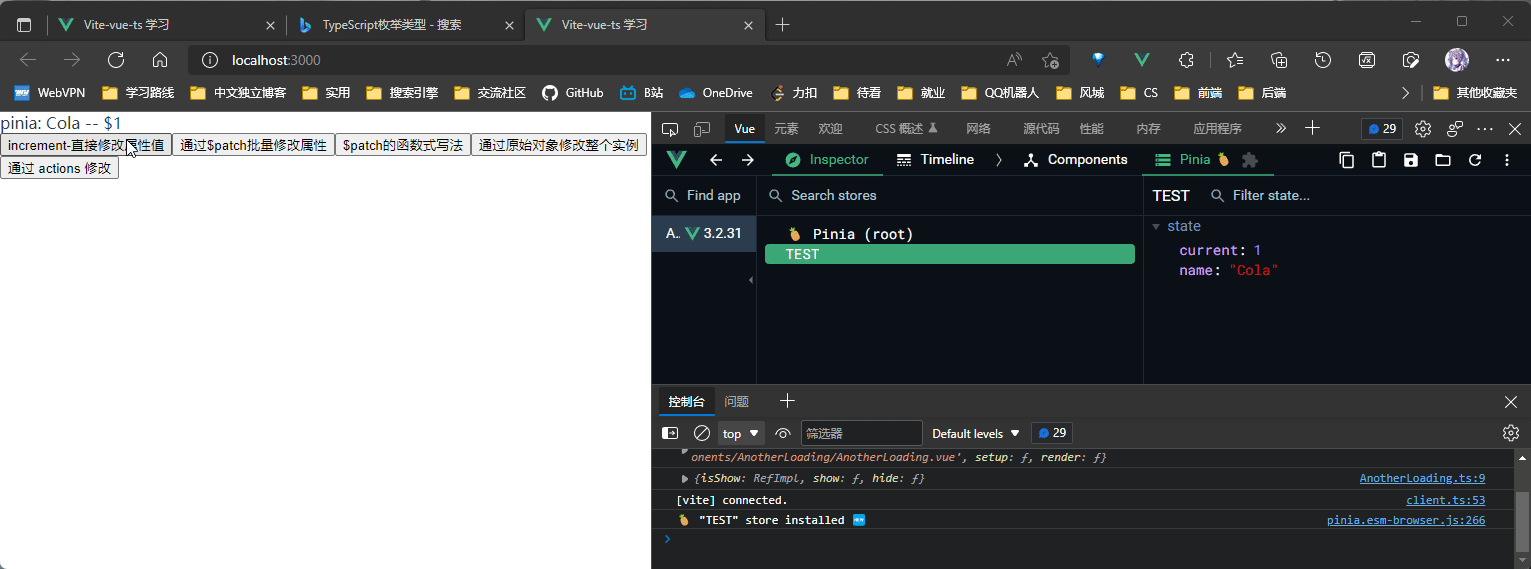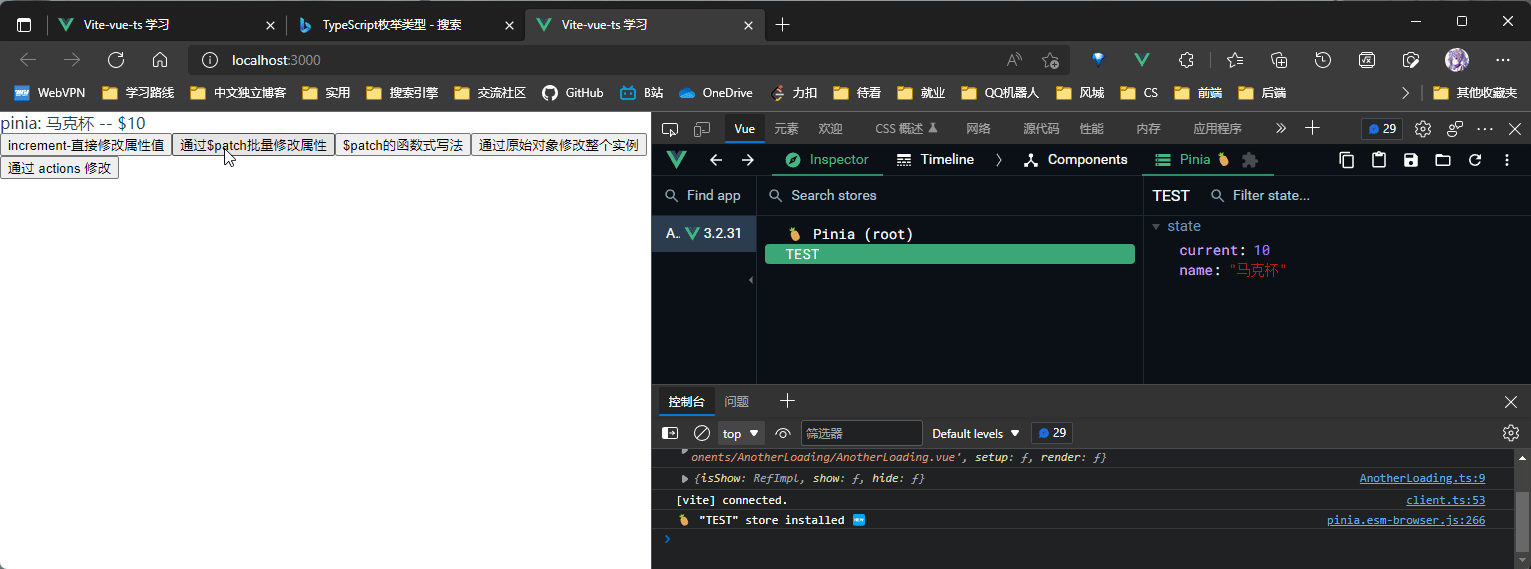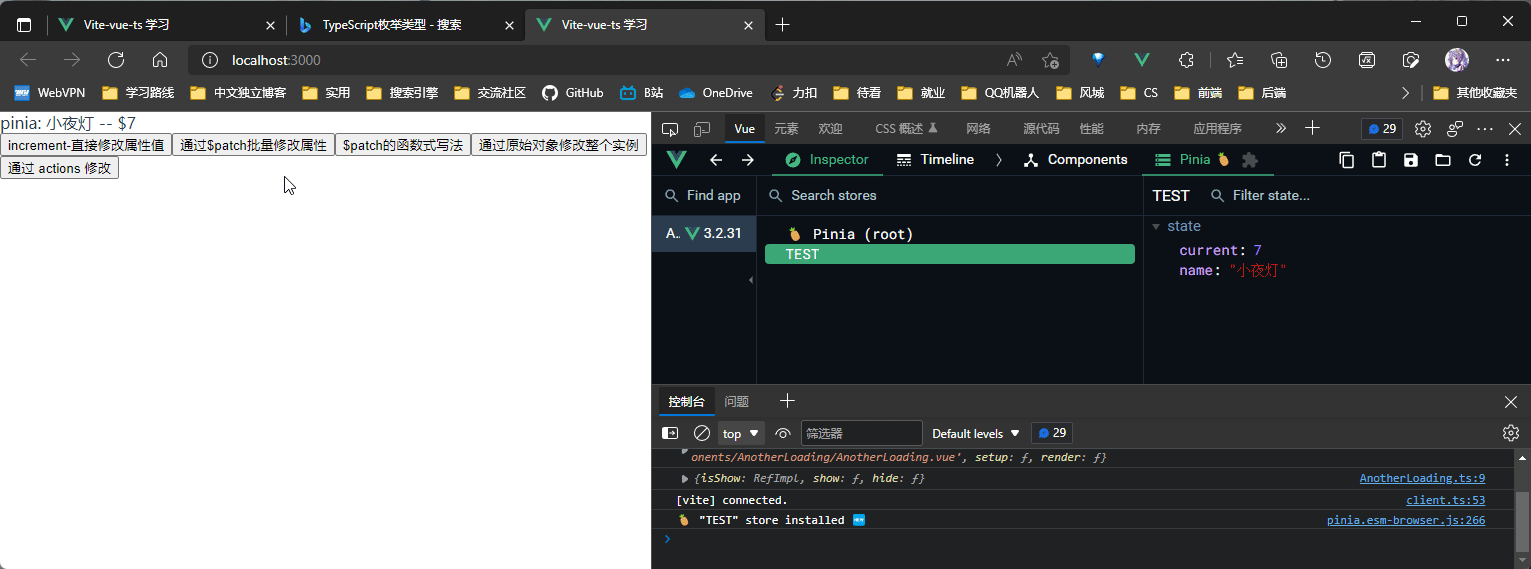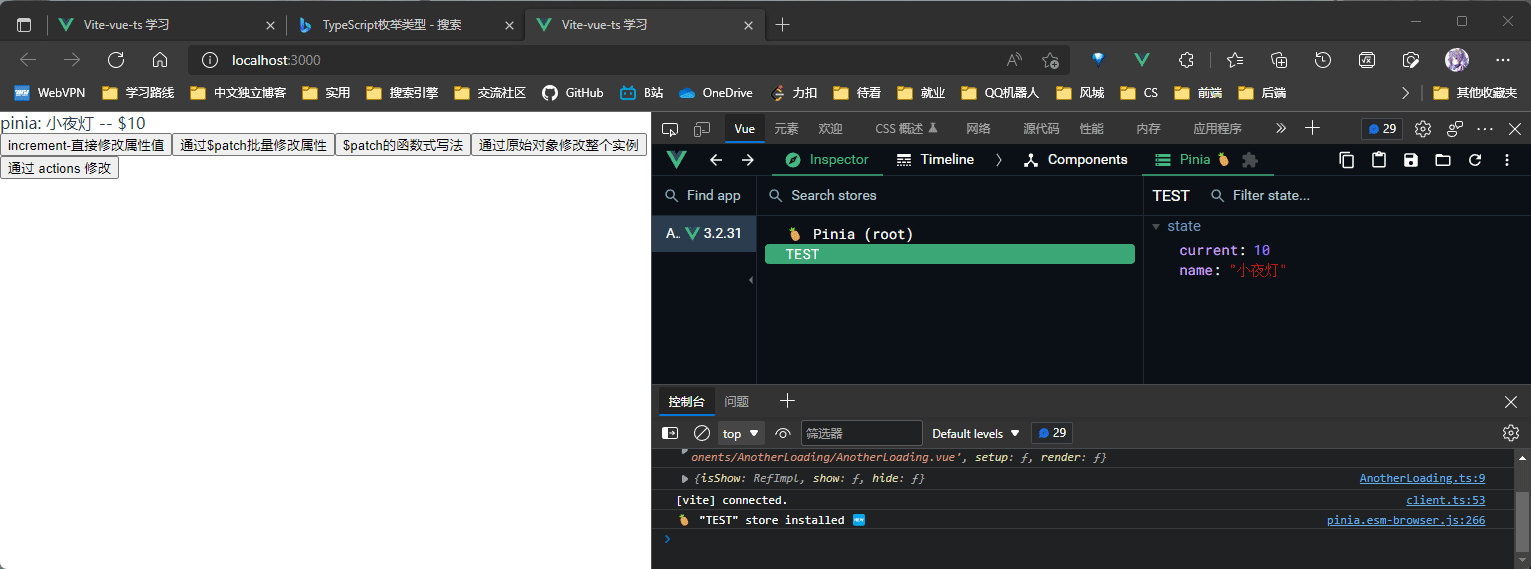
// 方法2: 通过$patch 批量修改属性值
const useTestChange2 = () => {
useTest.$patch({
name: "马克杯",
current: 10,
});
};
// 方法3: $patch 函数式写法
const useTestChange3 = () => {
useTest.$patch((state) => {
state.name = "立牌";
state.current = 5;
});
};
// 方法4: 通过原始对象修改整个实例(缺点在于需要修改state所有属性, 因此一般不建议使用)
const useTestChange4 = () => {
useTest.$state = {
name: "小夜灯",
current: 7,
};
};
// 方法5: 通过 actions 修改
const useTestChange5 = () => {
useTest.currentIncrement();
};
</script>
<template>
<div>pinia: {{ useTest.name }} -- ${{ useTest.current }}</div>
<button @click="useTestChange1">increment-直接修改属性值</button>
<button @click="useTestChange2">通过$patch批量修改属性</button>
<button @click="useTestChange3">$patch的函数式写法</button>
<button @click="useTestChange4">通过原始对象修改整个实例</button>
<button @click="useTestChange5">通过 actions 修改</button>
</template>
<style lang="less" scoped></style>
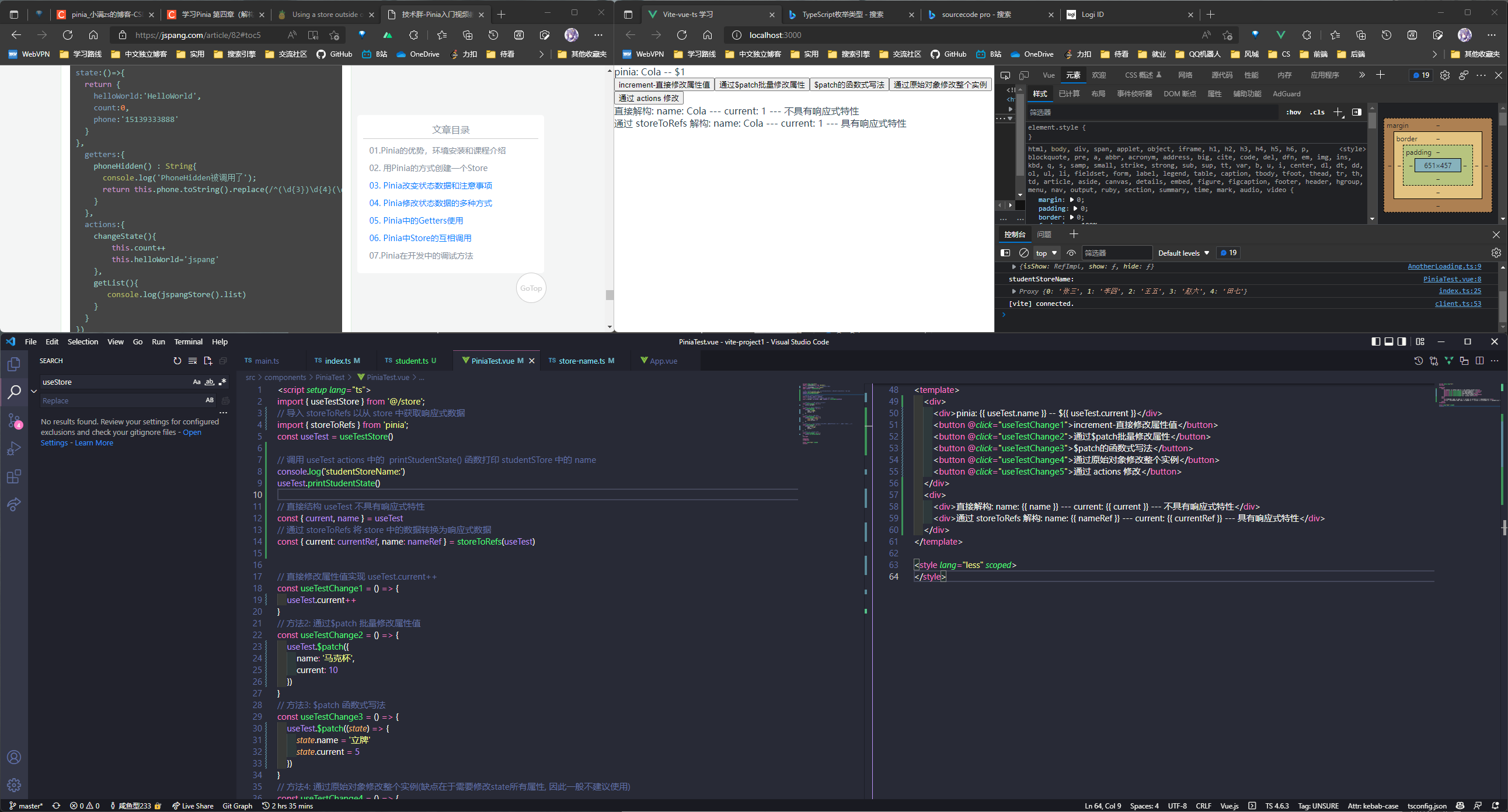
解构 store
学习 Pinia 第四章(解构 store) _小满 zs 的博客-CSDN 博客
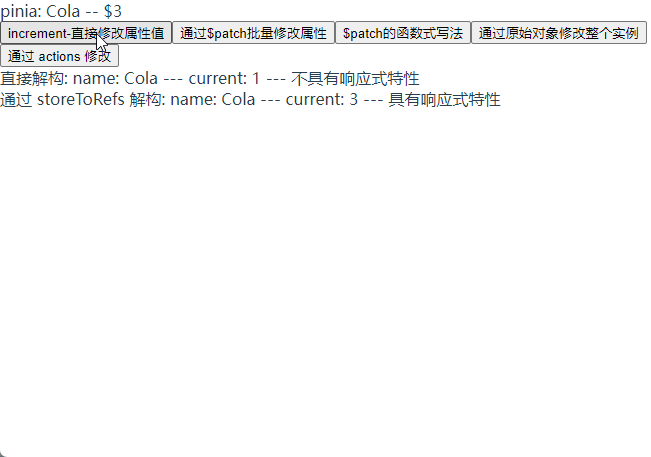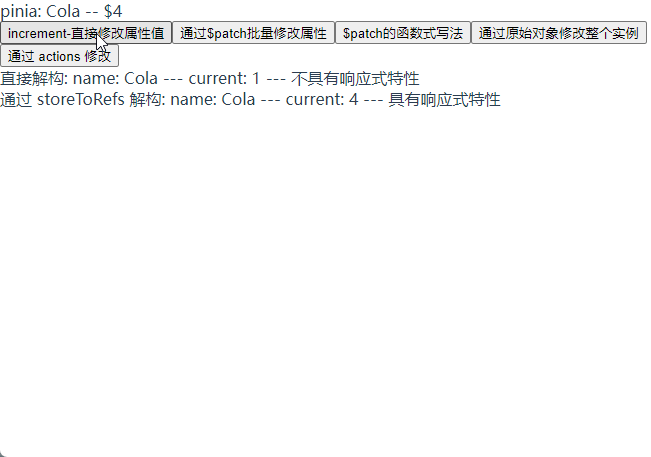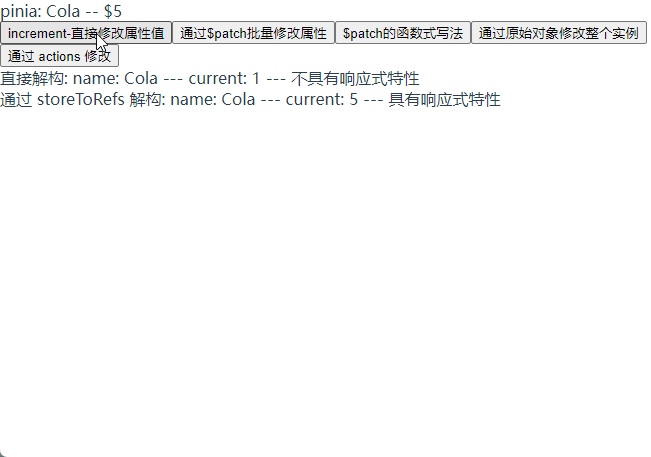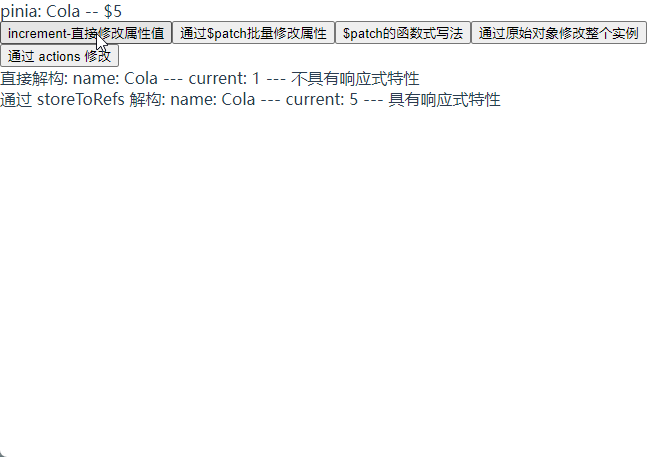
直接解构 store 的话没有响应性特性, 需要使用 storeToRefs 方法转换为响应式对象解构出来
<script setup lang="ts">
import { useTestStore } from "@/store";
// 导入 storeToRefs 以从 store 中获取响应式数据
import { storeToRefs } from "pinia";
const useTest = useTestStore();
// 直接结构 useTest 不具有响应式特性
const { current, name } = useTest;
// 通过 storeToRefs 将 store 中的数据转换为响应式数据
const { current: currentRef, name: nameRef } = storeToRefs(useTest);
// 直接修改属性值实现 useTest.current++
const useTestChange1 = () => {
useTest.current++;
};
// 方法2: 通过$patch 批量修改属性值
const useTestChange2 = () => {
useTest.$patch({
name: "马克杯",
current: 10,
});
};
// 方法3: $patch 函数式写法
const useTestChange3 = () => {
useTest.$patch((state) => {
state.name = "立牌";
state.current = 5;
});
};
// 方法4: 通过原始对象修改整个实例(缺点在于需要修改state所有属性, 因此一般不建议使用)
const useTestChange4 = () => {
useTest.$state = {
name: "小夜灯",
current: 7,
};
};
// 方法5: 通过 actions 修改
const useTestChange5 = () => {
useTest.currentIncrement();
};
</script>
<template>
<div>
<div>pinia: {{ useTest.name }} -- ${{ useTest.current }}</div>
<button @click="useTestChange1">increment-直接修改属性值</button>
<button @click="useTestChange2">通过$patch批量修改属性</button>
<button @click="useTestChange3">$patch的函数式写法</button>
<button @click="useTestChange4">通过原始对象修改整个实例</button>
<button @click="useTestChange5">通过 actions 修改</button>
</div>
<div>
<div>
直接解构: name: {{ name }} --- current: {{ current }} --- 不具有响应式特性
</div>
<div>
通过 storeToRefs 解构: name: {{ nameRef }} --- current:
{{ currentRef }} --- 具有响应式特性
</div>
</div>
</template>
<style lang="less" scoped></style>
原理和 toRefs 一样是给数据包一层toRef
在一个 store 中调用另一个 store 的方法和在 SFC 中调用 store 的方法一致:
store-name.ts:
export const enum Names {
TEST = "TEST",
STUDENT = "STUDENT",
}
student.ts:
import { defineStore } from "pinia";
import { Names } from "./store-name";
export const studentStore = defineStore(Names.STUDENT, {
state: () => {
return {
stuNames: ["张三", "李四", "王五", "赵六", "田七"],
};
},
});
index.ts:
import { defineStore } from "pinia";
import { Names } from "./store-name";
import { studentStore } from "./student";
export const useTestStore = defineStore(Names.TEST, {
// state 存储全局状态
state: () => {
return {
current: 1,
name: "Cola",
};
},
// computed like, 修饰一些值, 用于监视(计算)状态变化, 有缓存的功能
getters: {},
// methods, 可做同步异步, 提交state(用于修改 state 全局状态数据)
actions: {
// current++
currentIncrement() {
this.current++;
},
// 打印 studentStore 的 name
printStudentState() {
console.log(studentStore().stuNames);
},
},
});
PiniaTest.vue 代码片段:
import { useTestStore } from "@/store";
// 导入 storeToRefs 以从 store 中获取响应式数据
import { storeToRefs } from "pinia";
const useTest = useTestStore();
// 调用 useTest actions 中的 printStudentState() 函数打印 studentSTore 中的 name
console.log("studentStoreName:");
useTest.printStudentState();
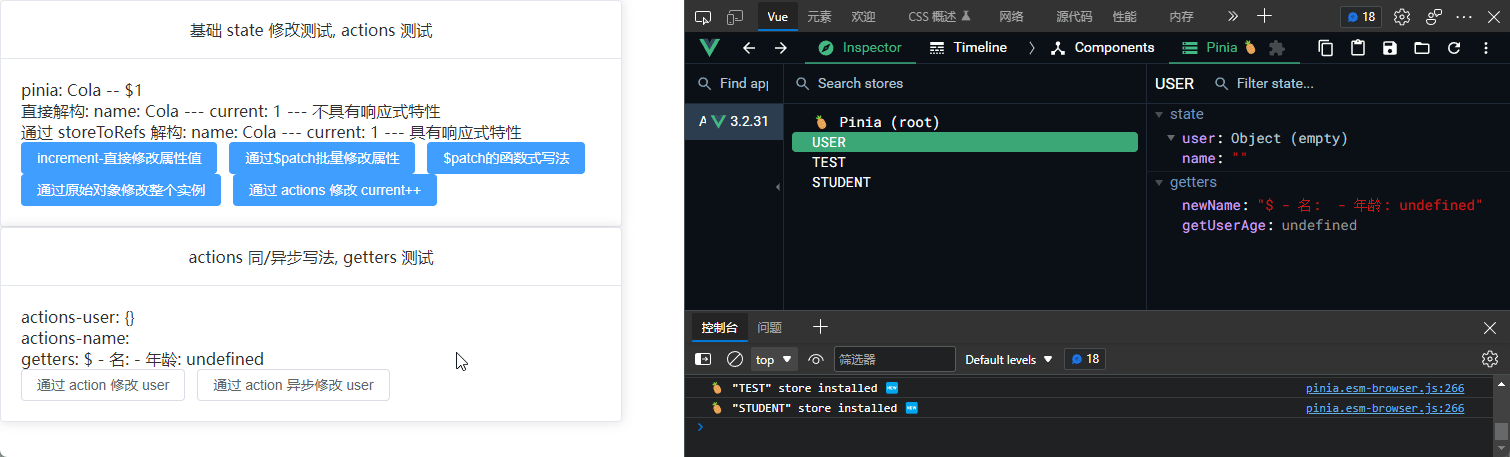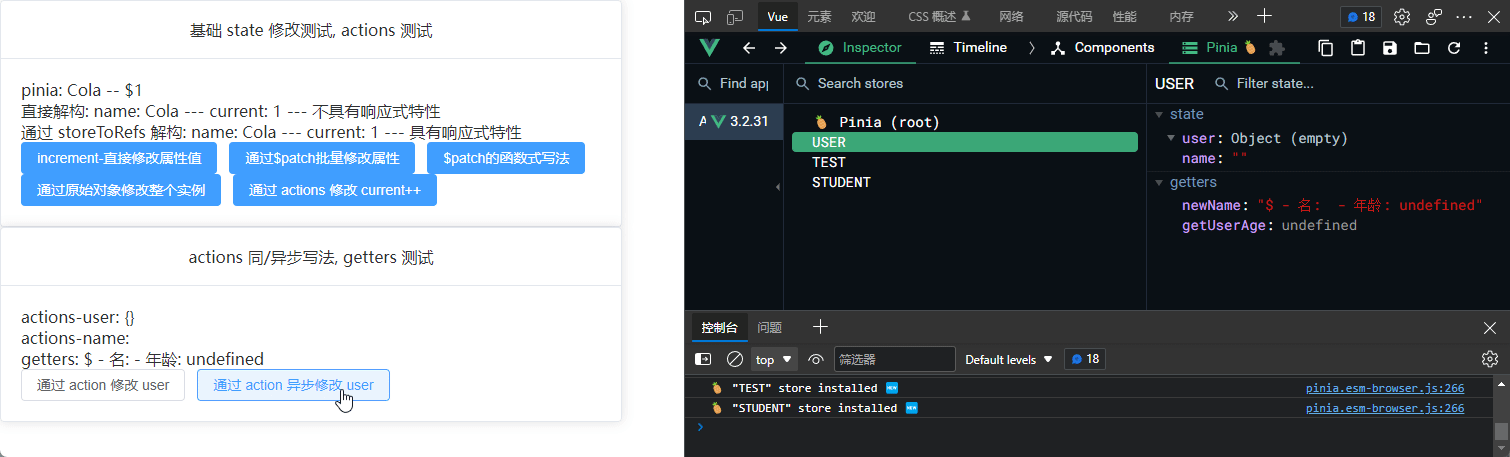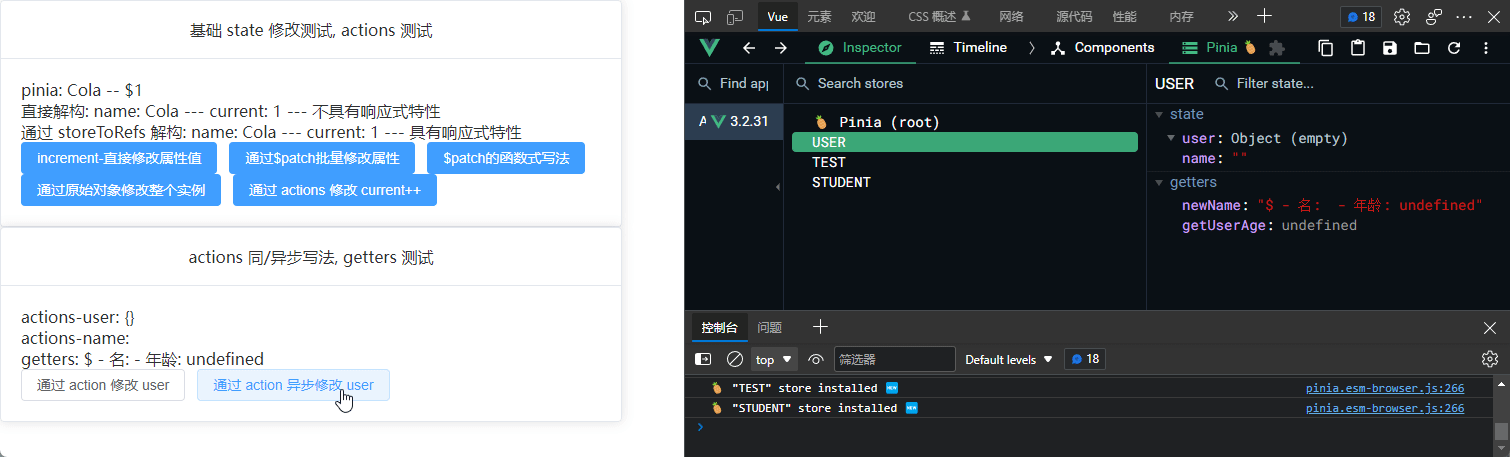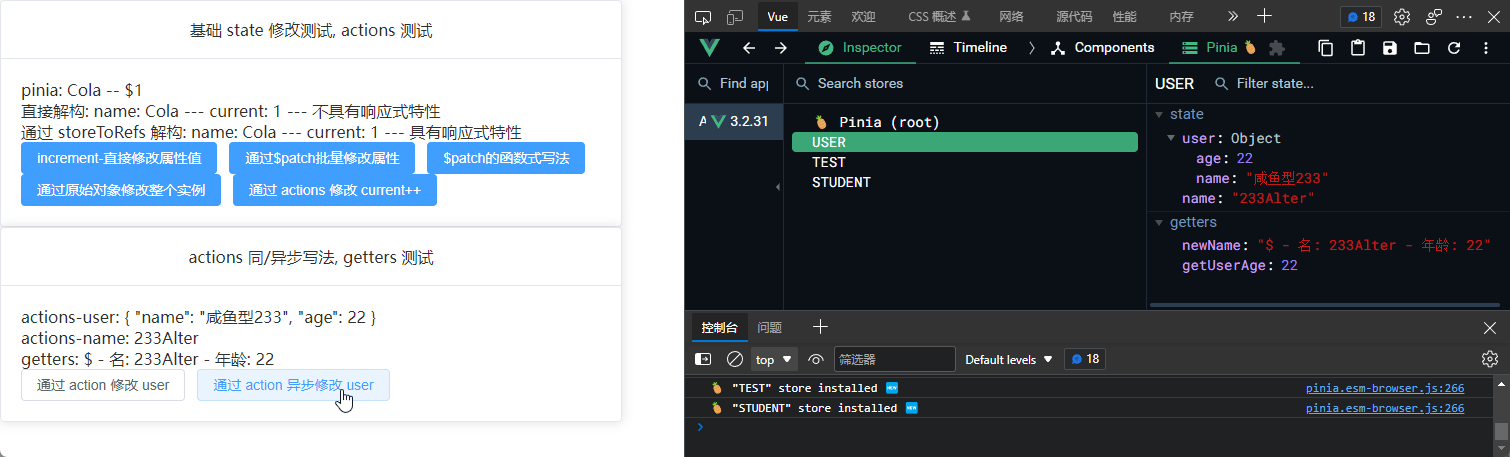
Actions, getters
Actions 同步写法
store-name.ts 片段:
export const enum Names {
USER = "USER",
}
User.ts:
import { defineStore } from "pinia";
import { Names } from "./store-name";
import { studentStore } from "./student";
type User = {
name: string;
age: number;
};
let result: User = {
name: "233",
age: 21,
};
export const userStore = defineStore(Names.USER, {
// state 存储全局状态
state: () => {
return {
user: <User>{},
name: "",
};
},
// computed like, 修饰一些值, 用于监视(计算)状态变化, 有缓存的功能
getters: {},
// methods, 可做同步异步, 提交state(用于修改 state 全局状态数据)
actions: {
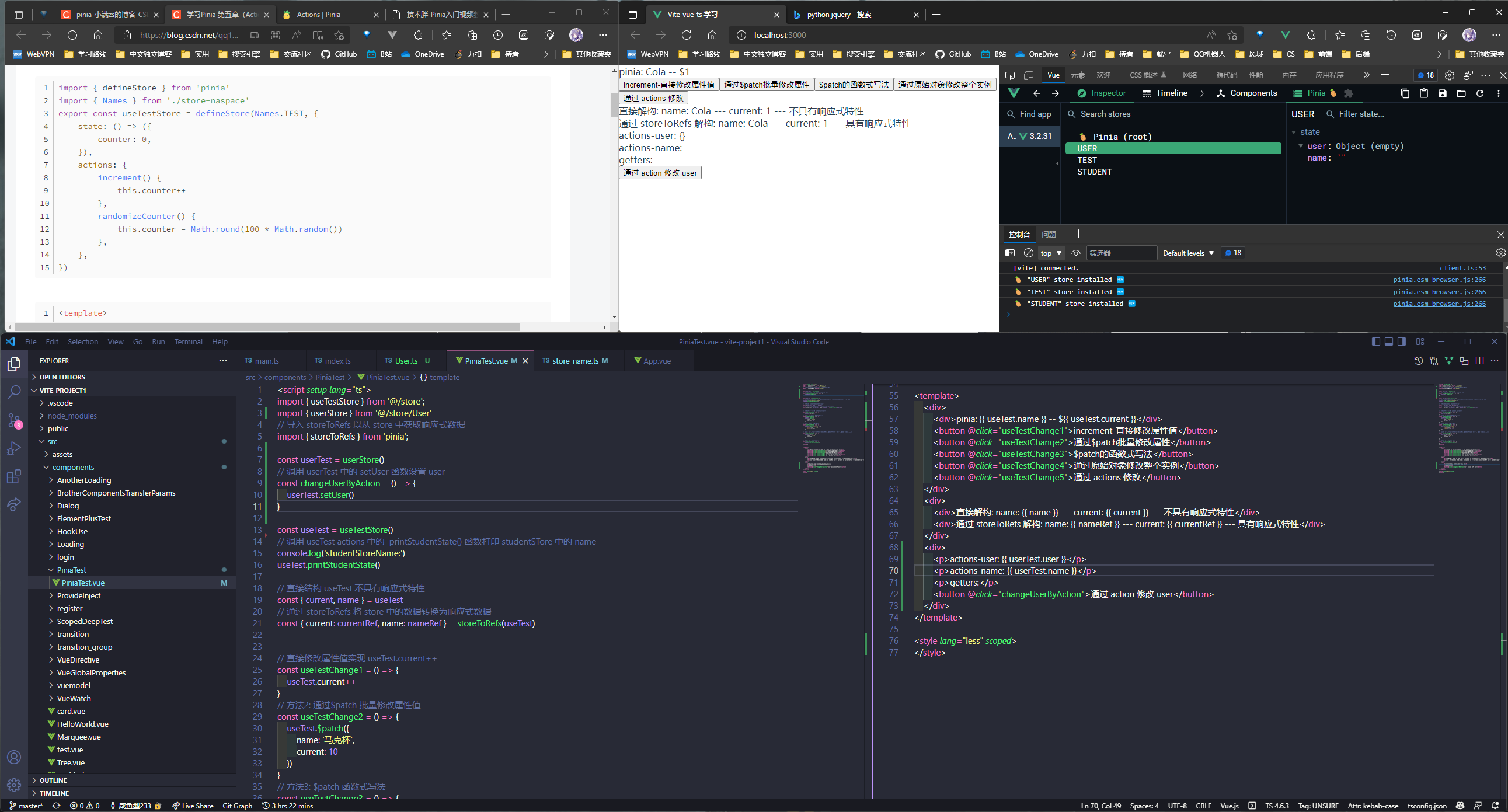
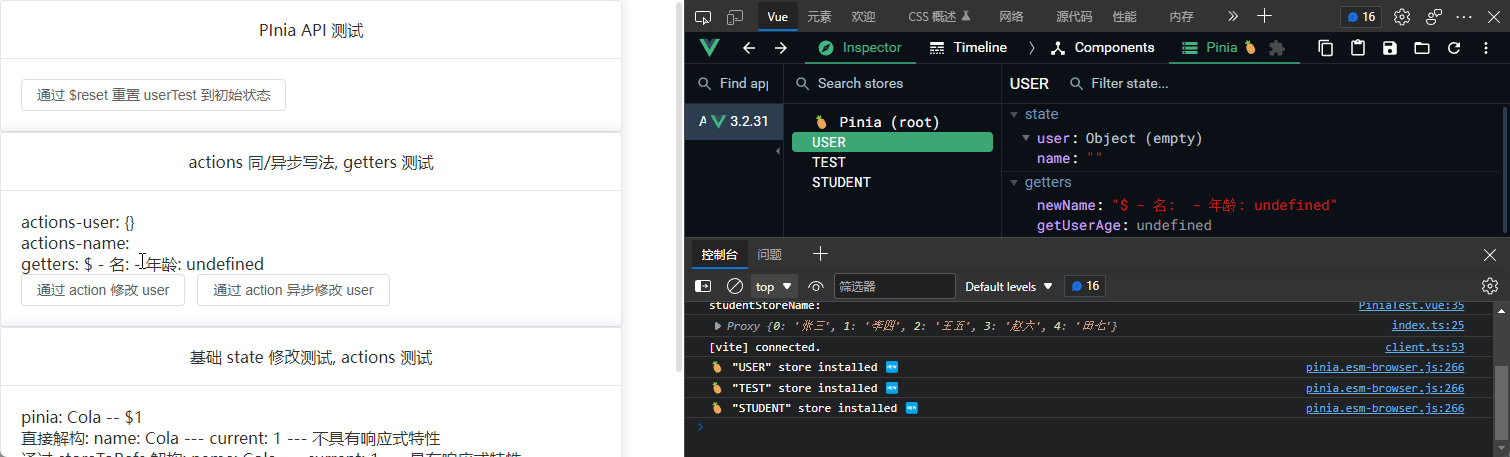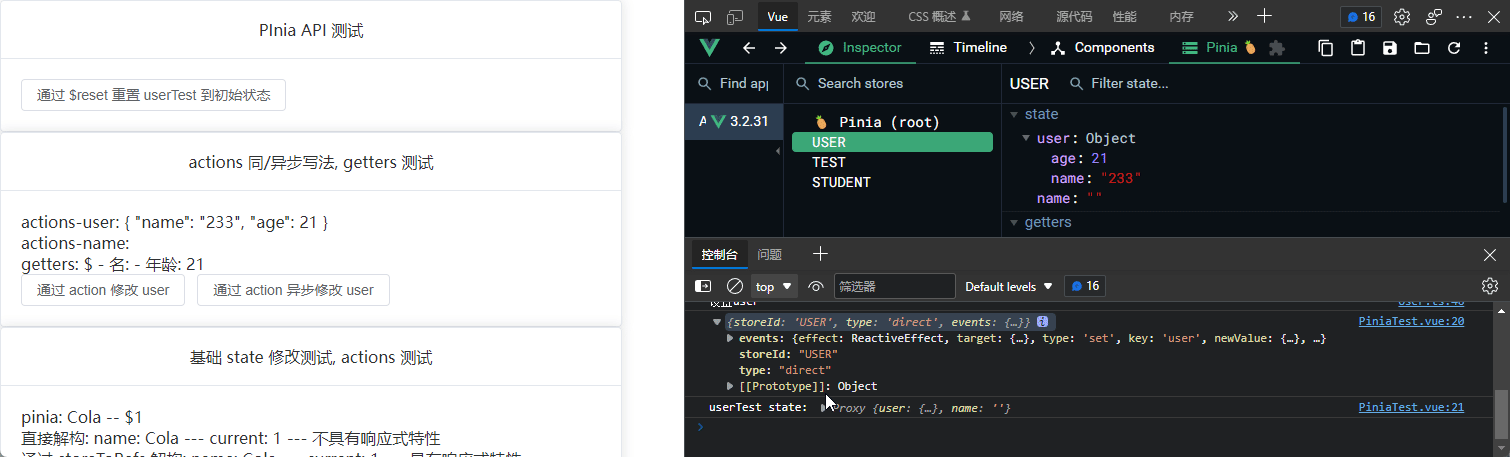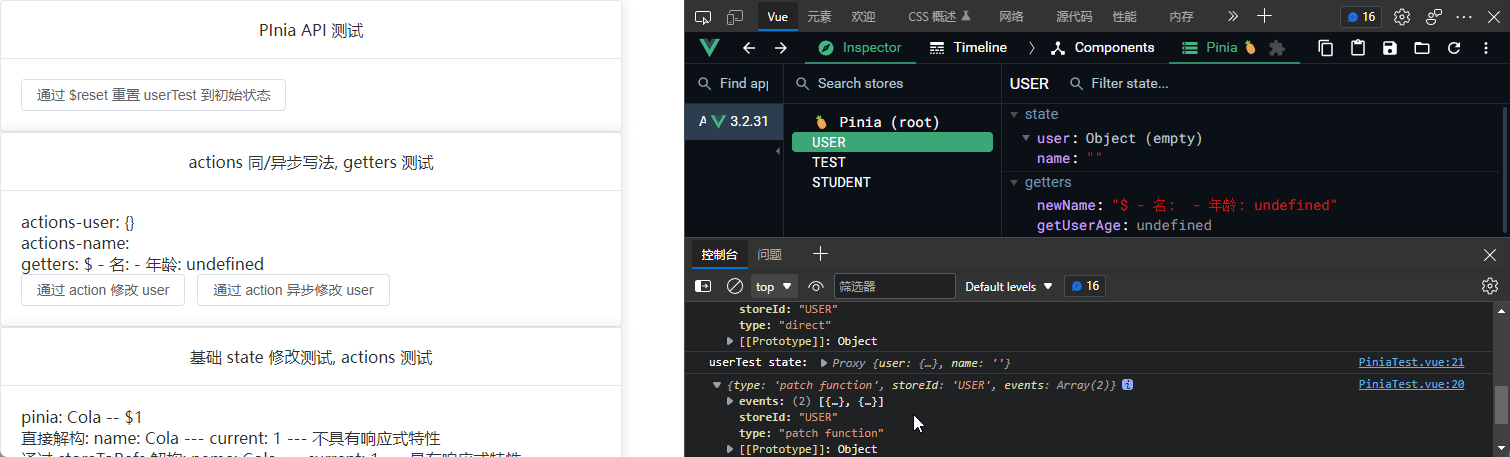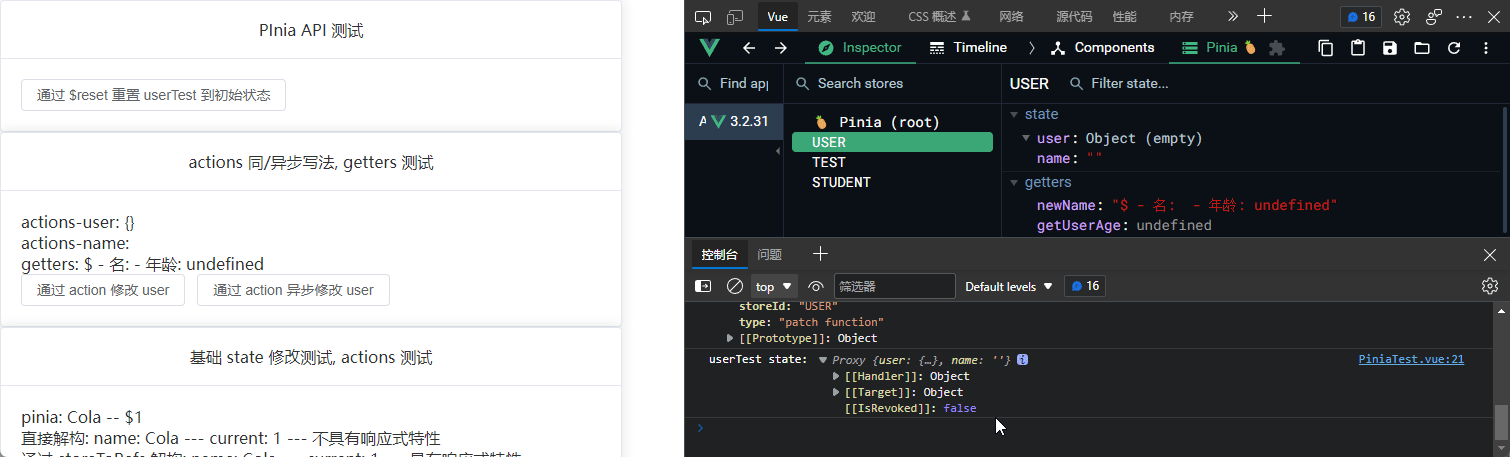
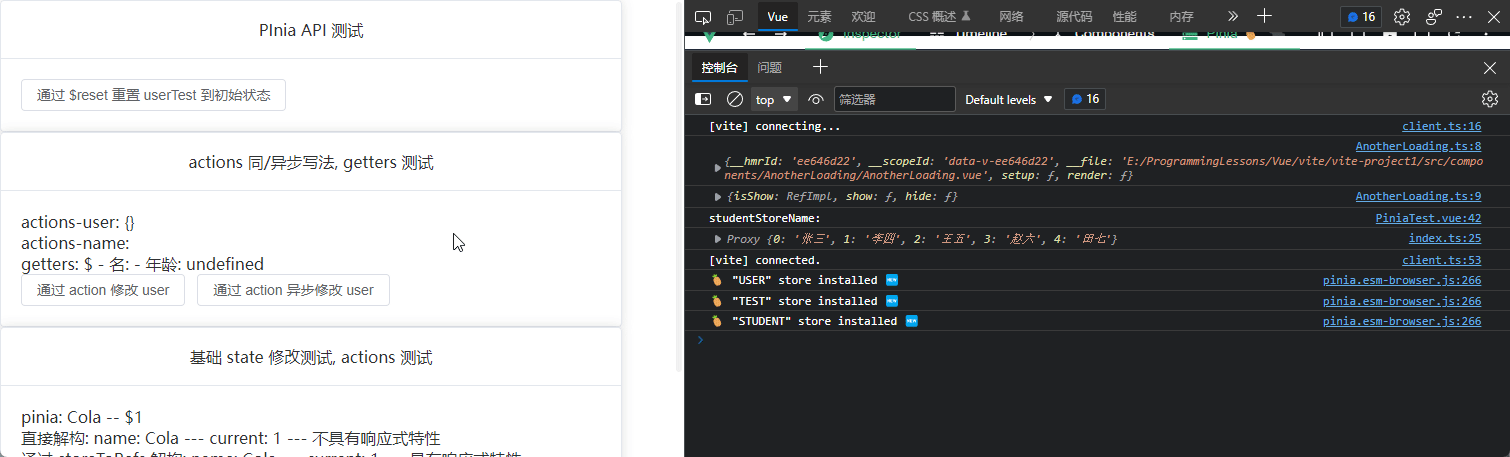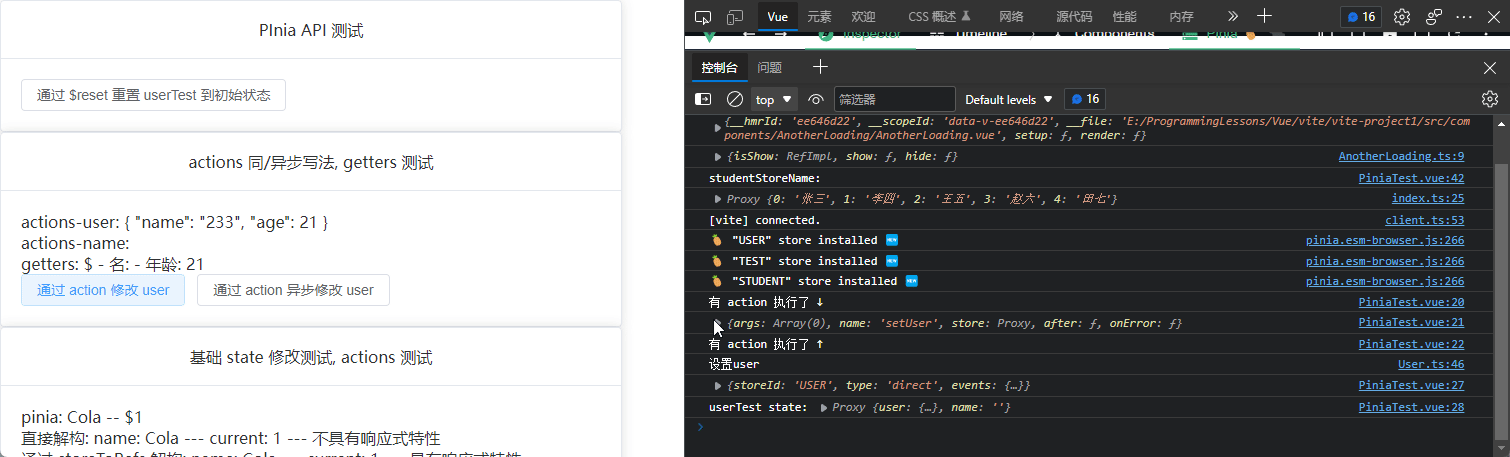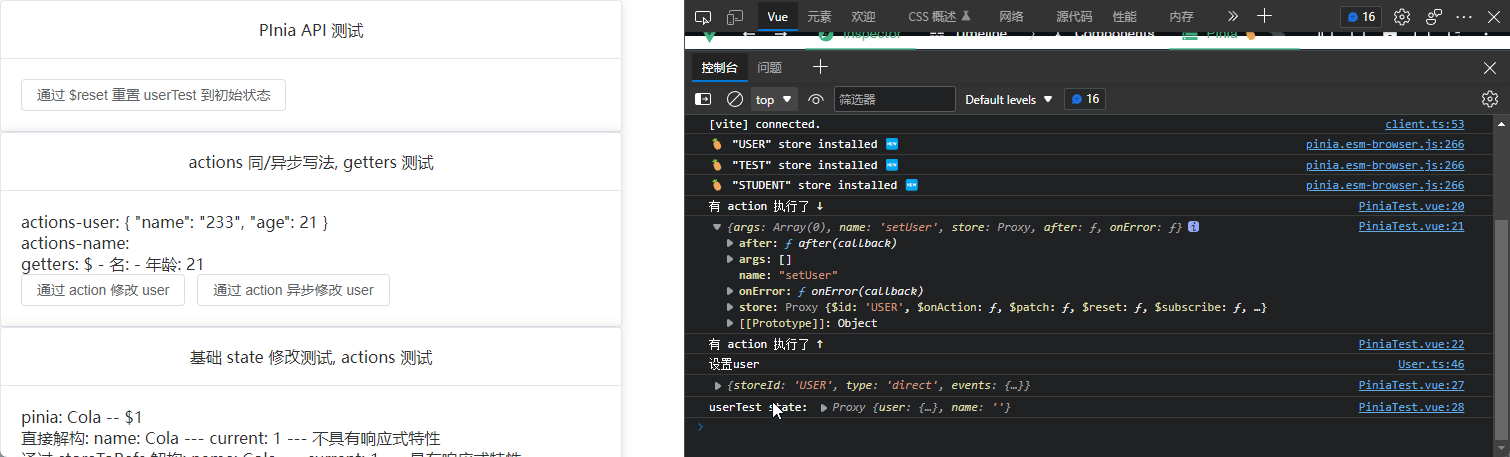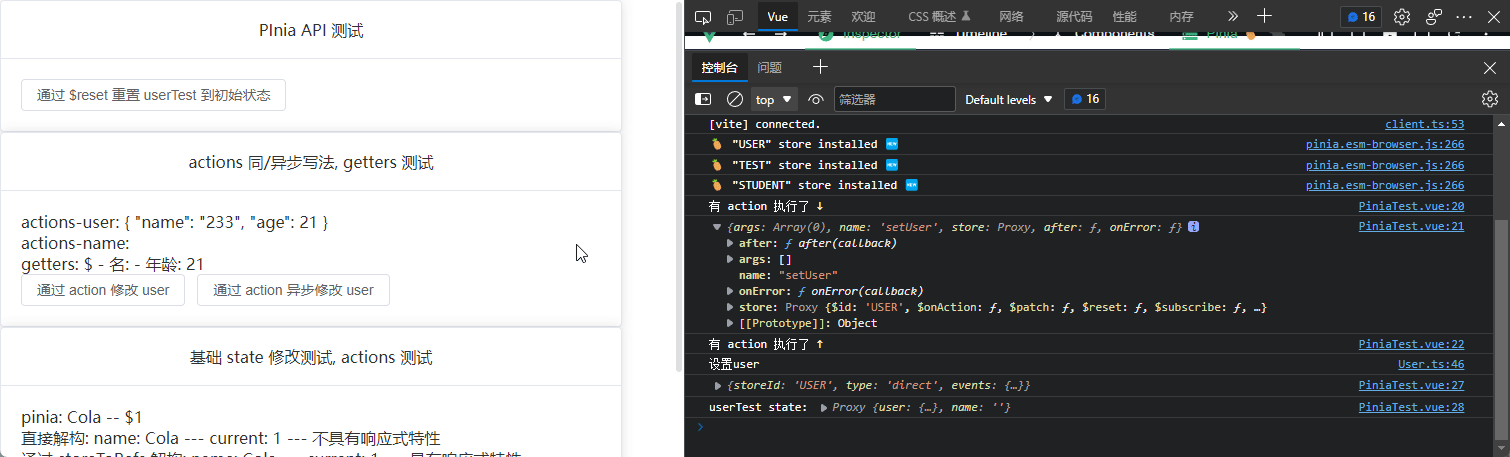
// 写个同步方法, setuser
setUser() {
console.log("设置user");
this.user = result;
},
},
});
PiniaTest.vue 片段:
import { userStore } from "@/store/User";
const userTest = userStore();
// 调用 userTest 中的 setUser 函数设置 user
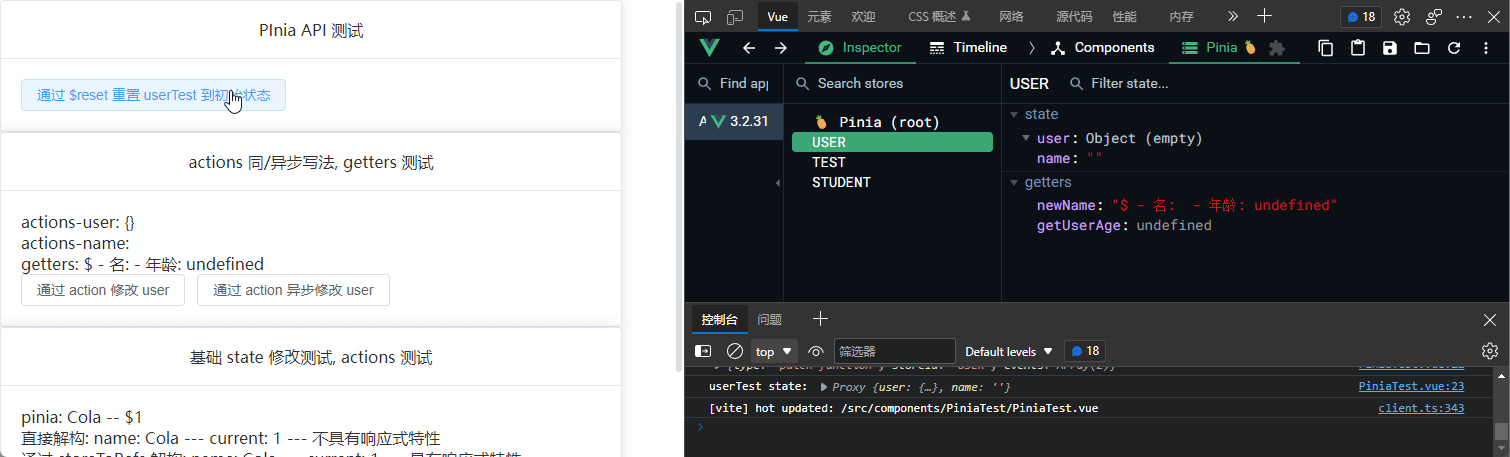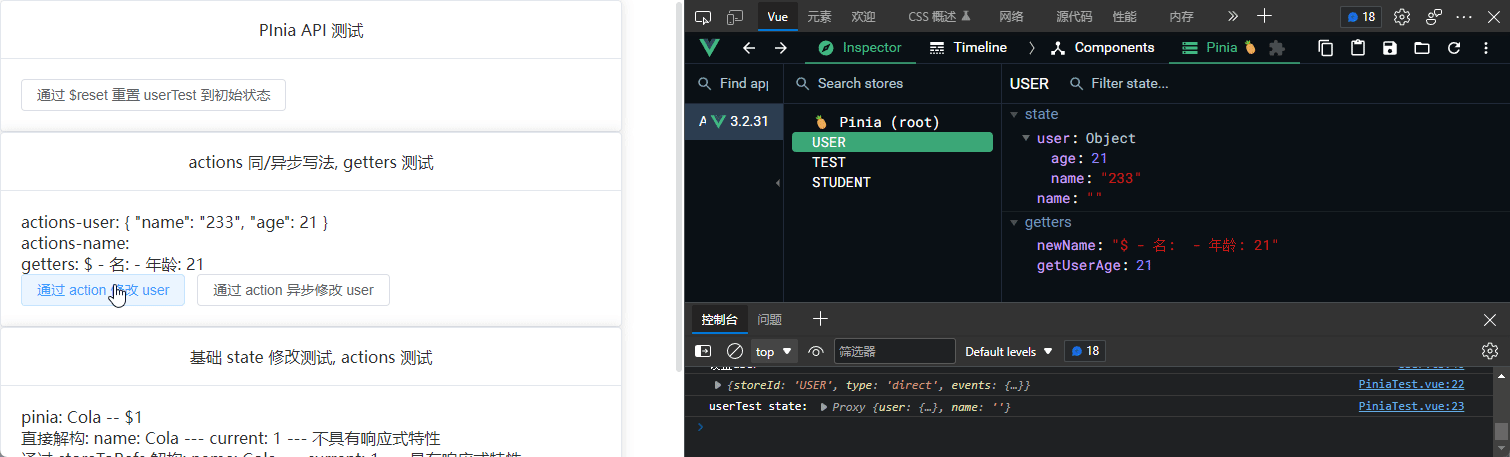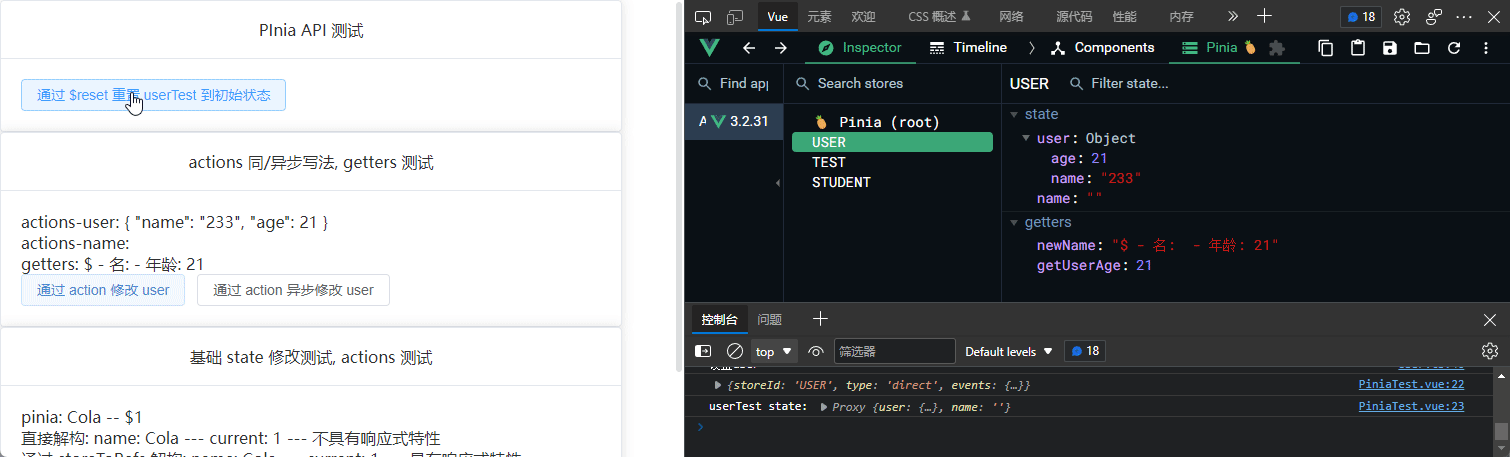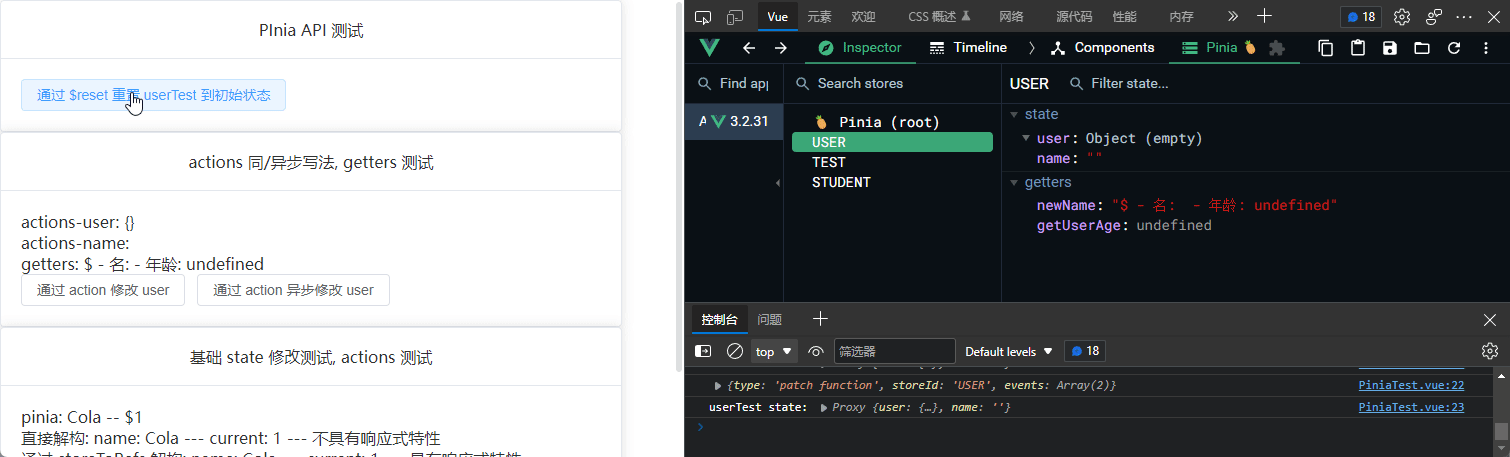
const changeUserByAction = () => {
userTest.setUser();
};
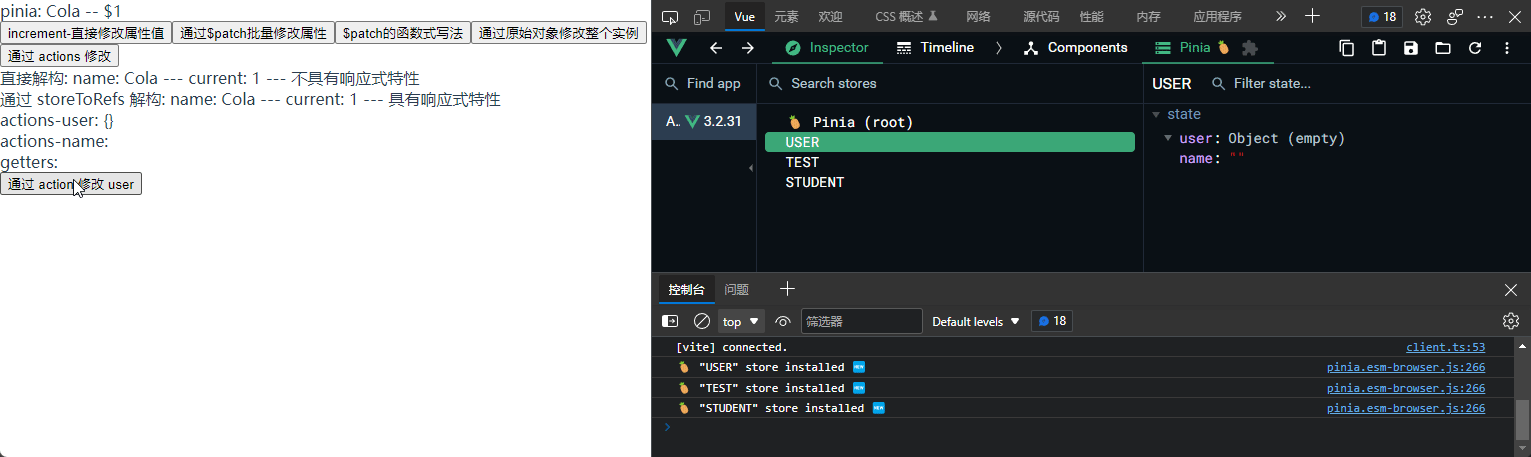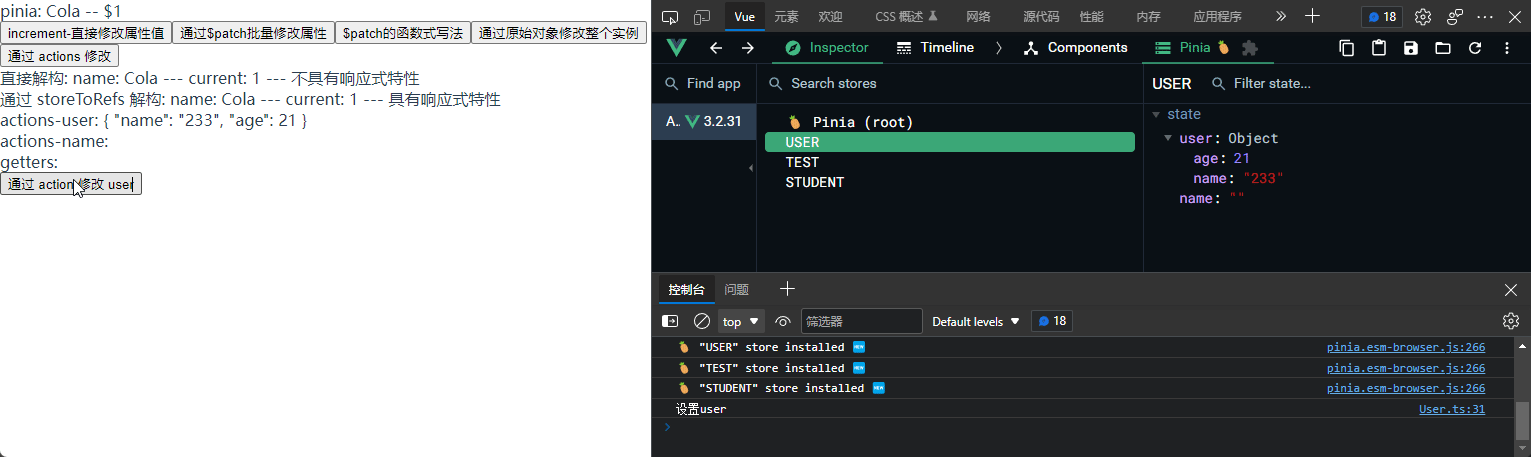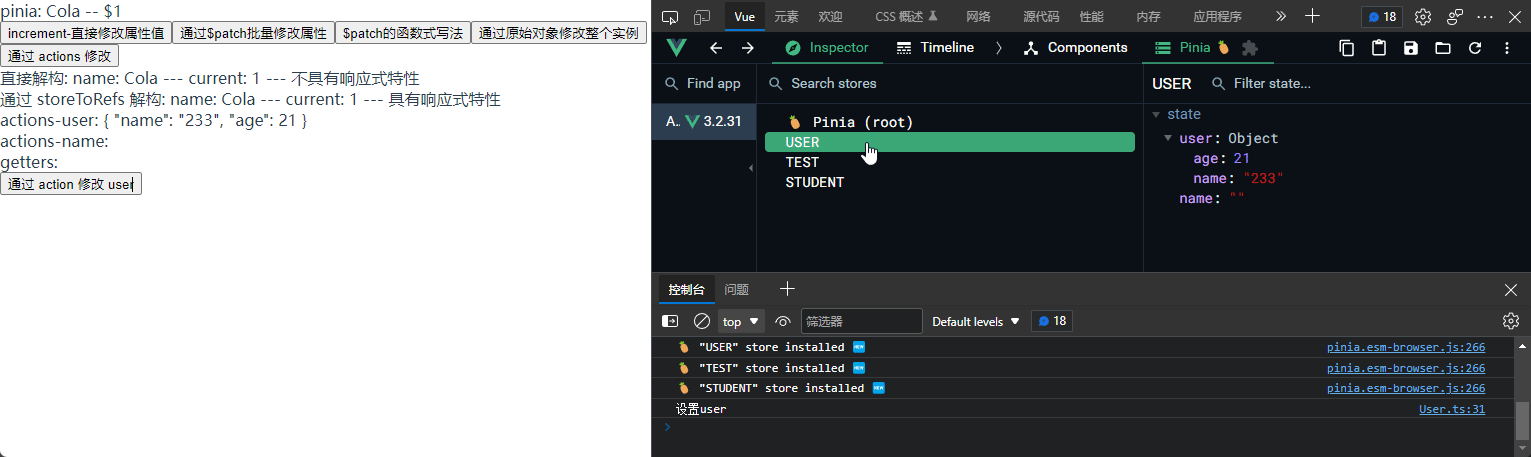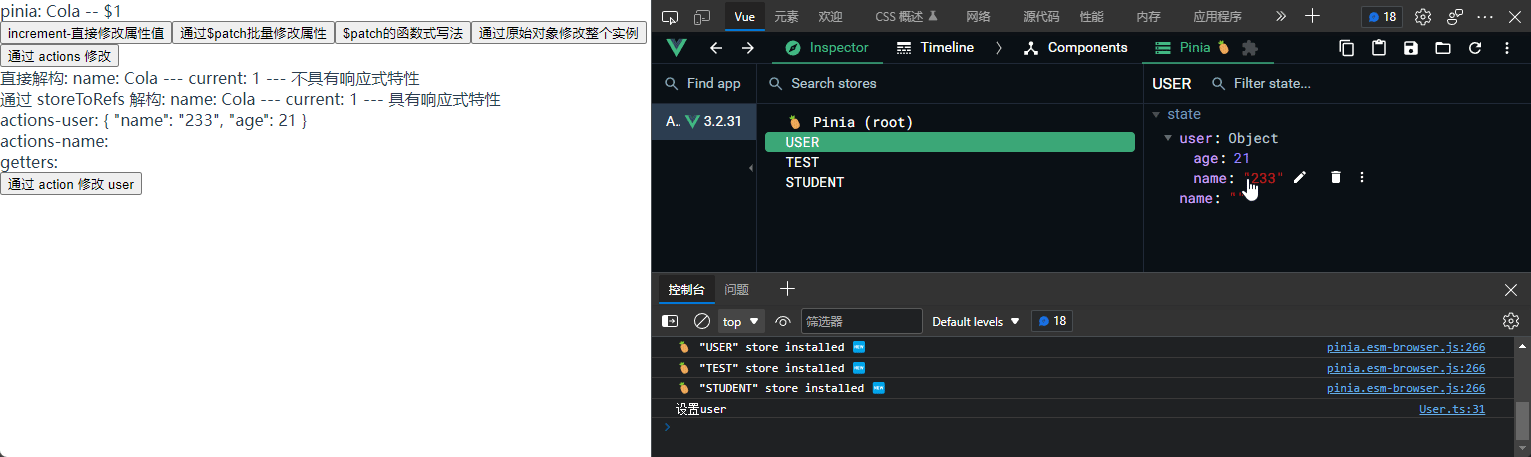
<div>
<p>actions-user: {{ userTest.user }}</p>
<p>actions-name: {{ userTest.name }}</p>
<p>getters:</p>
<button @click="changeUserByAction">通过 action 修改 user</button>
</div>
Actions 异步写法
user.ts 代码片段:
// 异步写法
async setUserAsync() {
const resultAsyn = await Login()
this.user = resultAsyn
this.setName("233Alter")
},
setName(name: string) {
this.name = name
}
PiniaTest.vue: 使用 ElementPlus 更新一波 UI:
<script setup lang="ts">
import { useTestStore } from "@/store";
import { userStore } from "@/store/User";
// 导入 storeToRefs 以从 store 中获取响应式数据
import { storeToRefs } from "pinia";
// element-plus button 相关依赖
import {
Check,
Delete,
Edit,
Message,
Search,
Star,
} from "@element-plus/icons-vue";
const userTest = userStore();
// 调用 userTest 中的 setUser 函数设置 user
const changeUserByAction = () => {
userTest.setUser();
};
// 调用 userTest 中的 setUserAsync 函数设置 user
const changeUserByActionAsync = () => {
userTest.setUserAsync();
};
const useTest = useTestStore();
// 调用 useTest actions 中的 printStudentState() 函数打印 studentSTore 中的 name
console.log("studentStoreName:");
useTest.printStudentState();
// 直接结构 useTest 不具有响应式特性
const { current, name } = useTest;
// 通过 storeToRefs 将 store 中的数据转换为响应式数据
const { current: currentRef, name: nameRef } = storeToRefs(useTest);
// 直接修改属性值实现 useTest.current++
const useTestChange1 = () => {
useTest.current++;
};
// 方法2: 通过$patch 批量修改属性值
const useTestChange2 = () => {
useTest.$patch({
name: "马克杯",
current: 10,
});
};
// 方法3: $patch 函数式写法
const useTestChange3 = () => {
useTest.$patch((state) => {
state.name = "立牌";
state.current = 5;
});
};
// 方法4: 通过原始对象修改整个实例(缺点在于需要修改state所有属性, 因此一般不建议使用)
const useTestChange4 = () => {
useTest.$state = {
name: "小夜灯",
current: 7,
};
};
// 方法5: 通过 actions 修改
const useTestChange5 = () => {
useTest.currentIncrement();
};
</script>
<template>
<div>
<el-card class="box-card">
<template #header>
<div class="card-header">基础 state 修改测试, actions 测试</div>
</template>
<el-row>pinia: {{ useTest.name }} -- ${{ useTest.current }}</el-row>
<el-row
>直接解构: name: {{ name }} --- current: {{ current }} ---
不具有响应式特性</el-row
>
<el-row
>通过 storeToRefs 解构: name: {{ nameRef }} --- current:
{{ currentRef }} --- 具有响应式特性</el-row
>
<el-row>
<el-button type="primary" @click="useTestChange1"
>increment-直接修改属性值</el-button
>
<el-button type="primary" @click="useTestChange2"
>通过$patch批量修改属性</el-button
>
<el-button type="primary" @click="useTestChange3"
>$patch的函数式写法</el-button
>
</el-row>
<el-row>
<el-button type="primary" @click="useTestChange4"
>通过原始对象修改整个实例</el-button
>
<el-button type="primary" @click="useTestChange5"
>通过 actions 修改 current++</el-button
>
</el-row>
</el-card>
</div>
<div>
<el-card class="box-card">
<template #header>
<div class="card-header">actions 同/异步写法, getters 测试</div>
</template>
<p>actions-user: {{ userTest.user }}</p>
<p>actions-name: {{ userTest.name }}</p>
<p>getters:</p>
<el-button @click="changeUserByAction">通过 action 修改 user</el-button>
<el-button @click="changeUserByActionAsync"
>通过 action 异步修改 user</el-button
>
</el-card>
</div>
</template>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.card-header {
// 文字居中
text-align: center;
}
.text {
font-size: 14px;
}
.item {
margin-bottom: 18px;
}
.box-card {
width: 620px;
}
</style>
getters
actions 可用于修改 state, 而 getters 可用于修饰 state 并返回修饰结果
User.ts 代码片段:
// computed like, 修饰一些值, 用于监视(计算)状态变化, 有缓存的功能
getters: {
newName(): string {
return `$ - 名: ${this.name} - 年龄: ${this.getUserAge}`
},
getUserAge(): number {
return this.user.age
}
},
PiniaTest.vue代码片段:
<el-card class="box-card">
<template #header>
<div class="card-header">actions 同/异步写法, getters 测试</div>
</template>
<p>actions-user: {{ userTest.user }}</p>
<p>actions-name: {{ userTest.name }}</p>
<p>getters: {{ userTest.newName }}</p>
<el-button @click="changeUserByAction">通过 action 修改 user</el-button>
<el-button @click="changeUserByActionAsync"
>通过 action 异步修改 user</el-button
>
</el-card>
PInia 插件
pinia 和 vuex 都有一个通病 页面刷新状态会丢失, 所以要做下持久化插件
main.ts 代码片段:
import { createApp, toRaw } from "vue";
import { createPinia, PiniaPluginContext } from "pinia";
type Options = {
key?: string;
};
// 默认配置
const __piniaKey__ = "yusummer";
// 将 key 存入 localstorage
const setStorage = (key: string, value: any) => {
localStorage.setItem(key, JSON.stringify(value));
};
// 根据 key 从 localstorage 获取数据
const getStorage = (key: string) => {
return localStorage.getItem(key)
? JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem(key) as string)
: null;
};
// 定义 pinia 插件
const piniaPlugin = (options: Options) => {
return (context: PiniaPluginContext) => {
const { store } = context;
// 从 localstorage 获取数据
const data = getStorage(`${options.key ?? __piniaKey__}-${store.$id}`);
console.log(data);
// state 有变化时, 将数据存入 localstorage
store.$subscribe(() => {
setStorage(
`${options.key ?? __piniaKey__}-${store.$id}`,
toRaw(store.$state)
);
});
console.log("store", store);
return {
...data,
};
};
};
// export const app = createApp(App)
const app = createApp(App);
// 使用 ElementPlus 插件
app.use(ElementPlus);
// 引入 pinia
const store = createPinia();
store.use(
piniaPlugin({
key: "pinia",
})
);
DailyNotes/HTML&CSS.md at main · Ayusummer/DailyNotes (github.com)
API
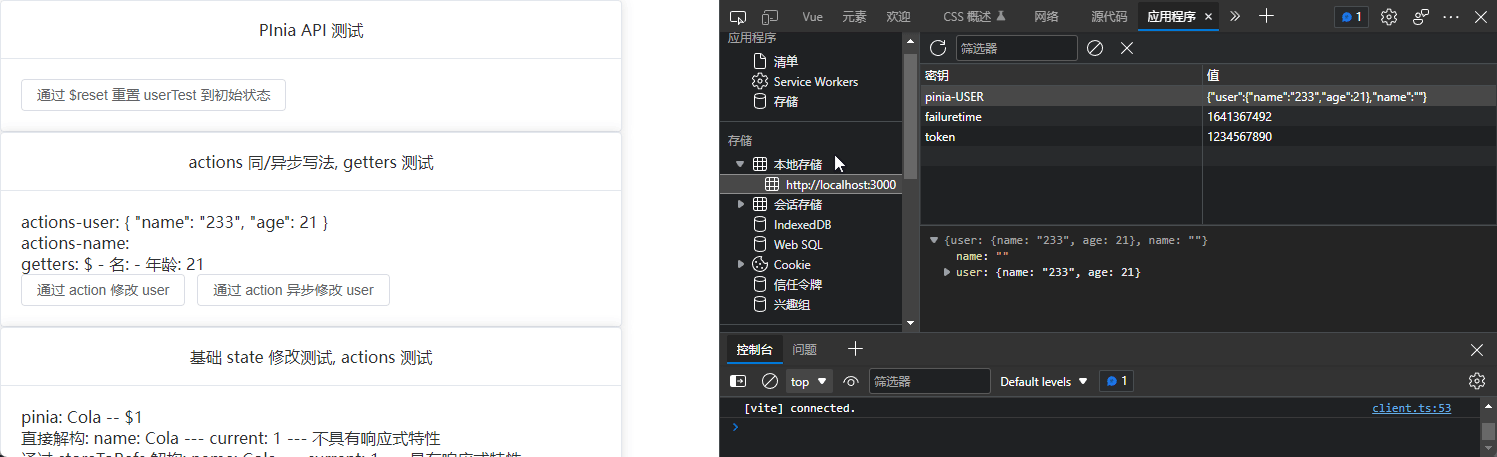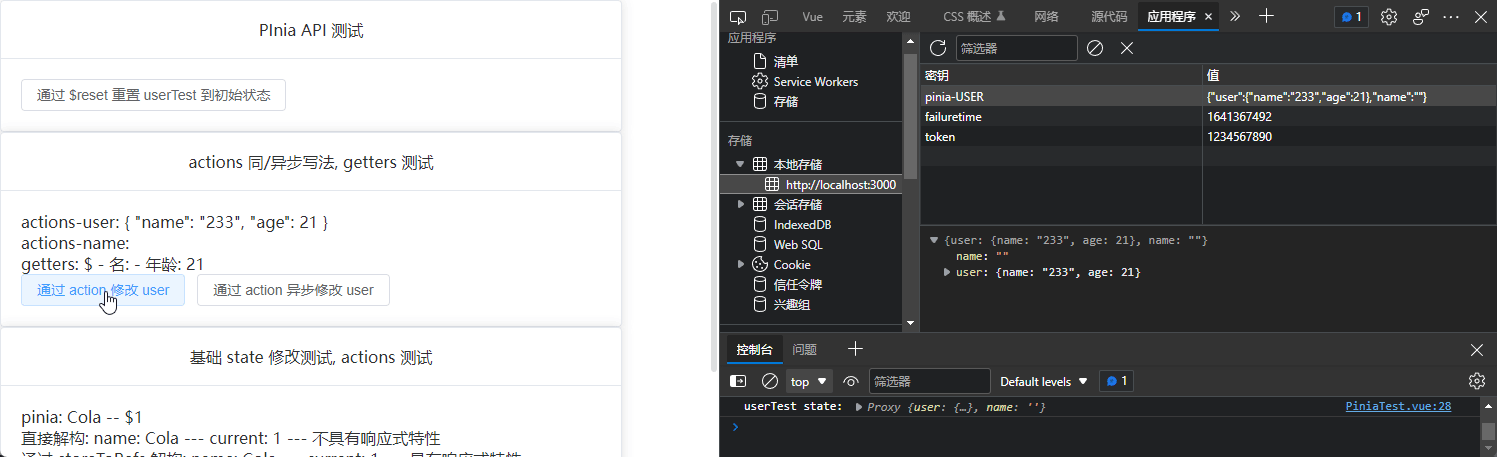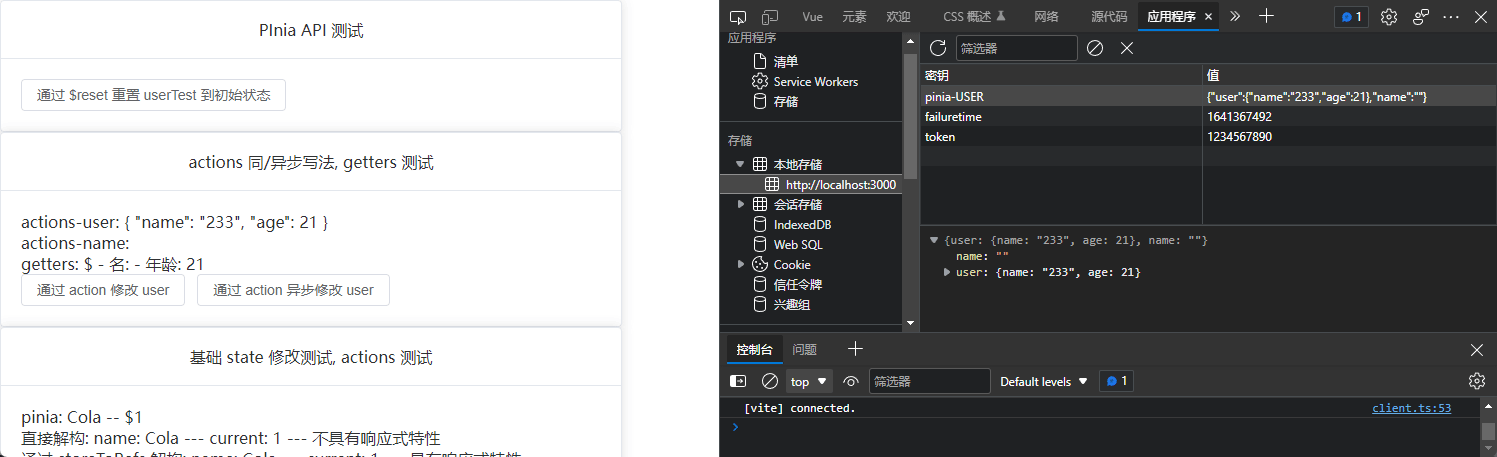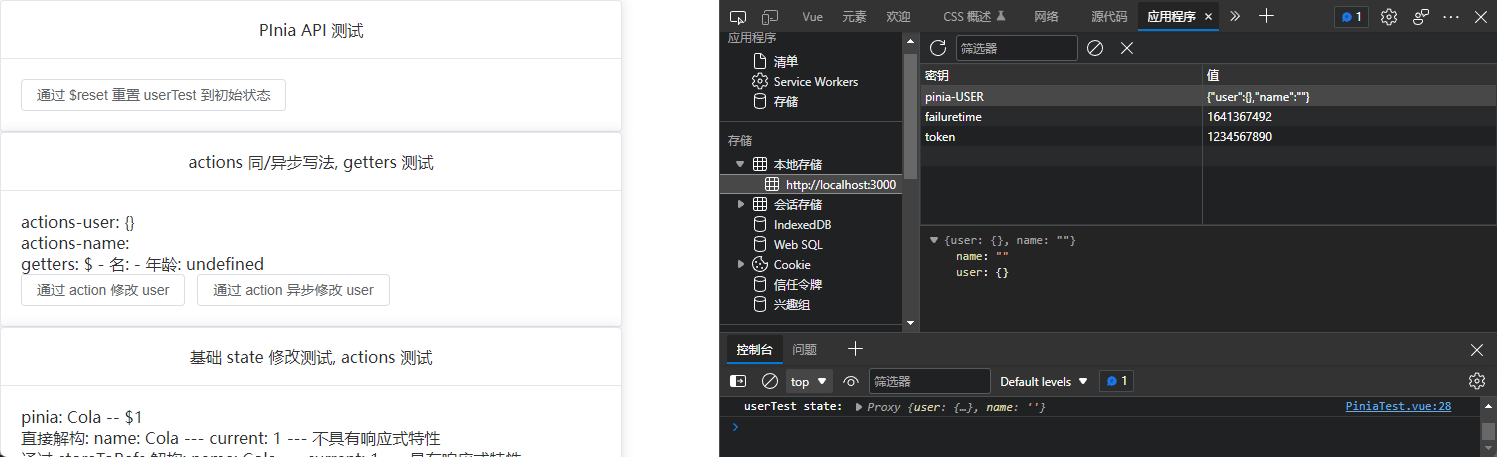
$reset
无参函数, 用于重置 state 状态
<el-button @click="userTest.$reset()"
>通过 $reset 重置 userTest 到初始状态</el-button
>
$subscribe
订阅 state 更新
PiniaTest.vue 代码片段:
// 通过 $subscribe 订阅 state 的改变
userTest.$subscribe((args, state) => {
console.log(args);
console.log("userTest state:", state);
});
$subscribe还有第二个参数, 目前暂时没用到就没做记录, 详见学习 Pinia 第六章(API) _小满 zs 的博客-CSDN 博客
$onAction
只要有 action 被调用就会执行该函数
PiniaTest.vue 代码片段:
// 当有 action 执行时便会执行 $onAction 函数
userTest.$onAction((args) => {
console.log("有 action 执行了 ↓");
console.log(args);
console.log("有 action 执行了 ↑");
});
$onAction还有第二个参数, 目前暂时没用到就没做记录, 详见学习 Pinia 第六章(API) _小满 zs 的博客-CSDN 博客