响应模型
大约 7 分钟
响应模型
response_model
使用 pydantic.BaseModel 派生子类创建响应模型类, 在写路由时使用 response_model=xxx 来指定 xxx 为响应模型, 这样返回的响应就是一个 xxx 实例
class UserBase(BaseModel):
username: str
email: EmailStr
mobile: str = "10086"
address: str = None
full_name: Optional[str] = None
class UserIn(UserBase):
"""用于创建 User 对象
用户创建时需要给出 password
但是访问用户时不应当返回 password
"""
password: str
class UserOut(UserBase):
pass
users = {
"user01": {"username": "user01", "password": "123123", "email": "user01@example.com"},
"user02": {"username": "user02", "password": "123456", "email": "user02@example.com", "mobile": "110"}
}
# 使用响应模型
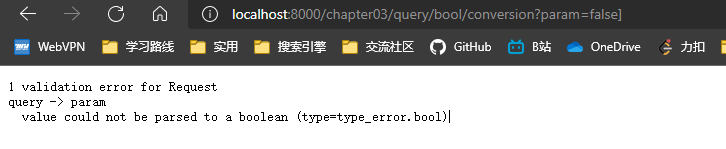
@app04.post("/response_model/", response_model=UserOut, response_model_exclude_unset=True)
async def response_model(user: UserIn):
"""
response_model_exclude_unset=True 表示默认值不包含在响应中, 仅包含实际给的值,
如果实际给的值与默认值相同也会包含在响应中
"""
print(user.password) # password不会被返回
# return user
return users["user02"]
@app04.post(
"/response_model/attributes",
# response_model=UserOut,
# response_model=Union[UserIn, UserOut], # 取并集(也就是两个类的属性都有)
response_model=List[UserOut],
# 包含某些字段, 这里的 mobile 会被下面 exclude 覆盖掉
# response_model_include=["username", "email", "mobile"],
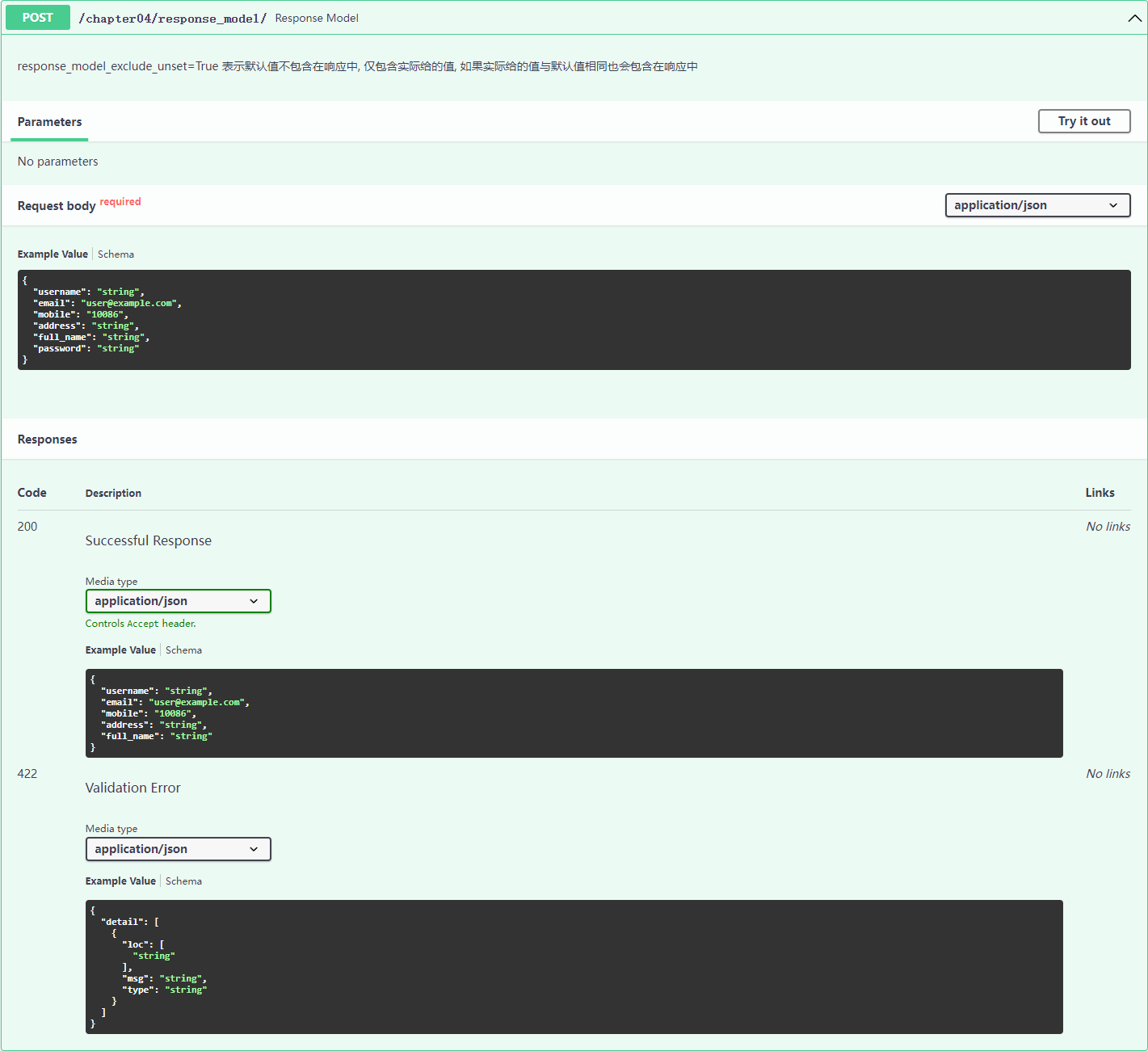
response_model_include=["username", "email"], # 包含某些字段
response_model_exclude=["mobile"] # 排除掉某些字段
)
async def response_model_attributes(user: UserIn):
"""response_model_include列出需要在返回结果中包含的字段
response_model_exclude列出需要在返回结果中排除的字段
"""
# del user.password # Union[UserIn, UserOut]后,删除password属性也能返回成功
# return user
return [user, user]
响应模型可以使用单个响应模型类, 也可以使用模型类并集, 模型类列表;
响应模型亦可以进行特定字段的选取与排除
复杂类型响应
比如这种响应:

首先这是从数据库中获取到的数据加上一些修饰得到的
实现这种需求的两种方式:
直接搓 JSON
# 引入 jsonable_encoder
from fastapi.encoders import jsonable_encoder
from fastapi.responses import JSONResponse
staffs = crud.read_staff_by_page(db, page, pageSize)
staffs = list(jsonable_encoder(staffs))
return JSONResponse(content={
"code":0,
"message":"ok",
"result":{
"items":staffs,
"total": len(staffs)
},
"type":"success"
})
封装 schema
先用 pydantic.BaseModel 和 staff schema 封装一个响应模型类
# 虚拟一个默认员工
default_staff = {
"sid": 0,
"sname": "咸鱼型233",
"did": 0
}
class ResultSchema(BaseModel):
"""结果类"""
items: List[Staff] = [Staff(**default_staff)]
total: int = len(items)
# StaffListGetResultModel
class StaffListGetResultModel(BaseModel):
"""员工列表获取结果类
:param items: 员工列表; 默认值: [default_staff]
:param total: 员工总数; 默认值: 1
"""
code: int = 0
message: str = "ok"
result: ResultSchema = ResultSchema(**default_staff)
type: str = "success"
然后再返回需要从数据库中读取的数据以及默认值:
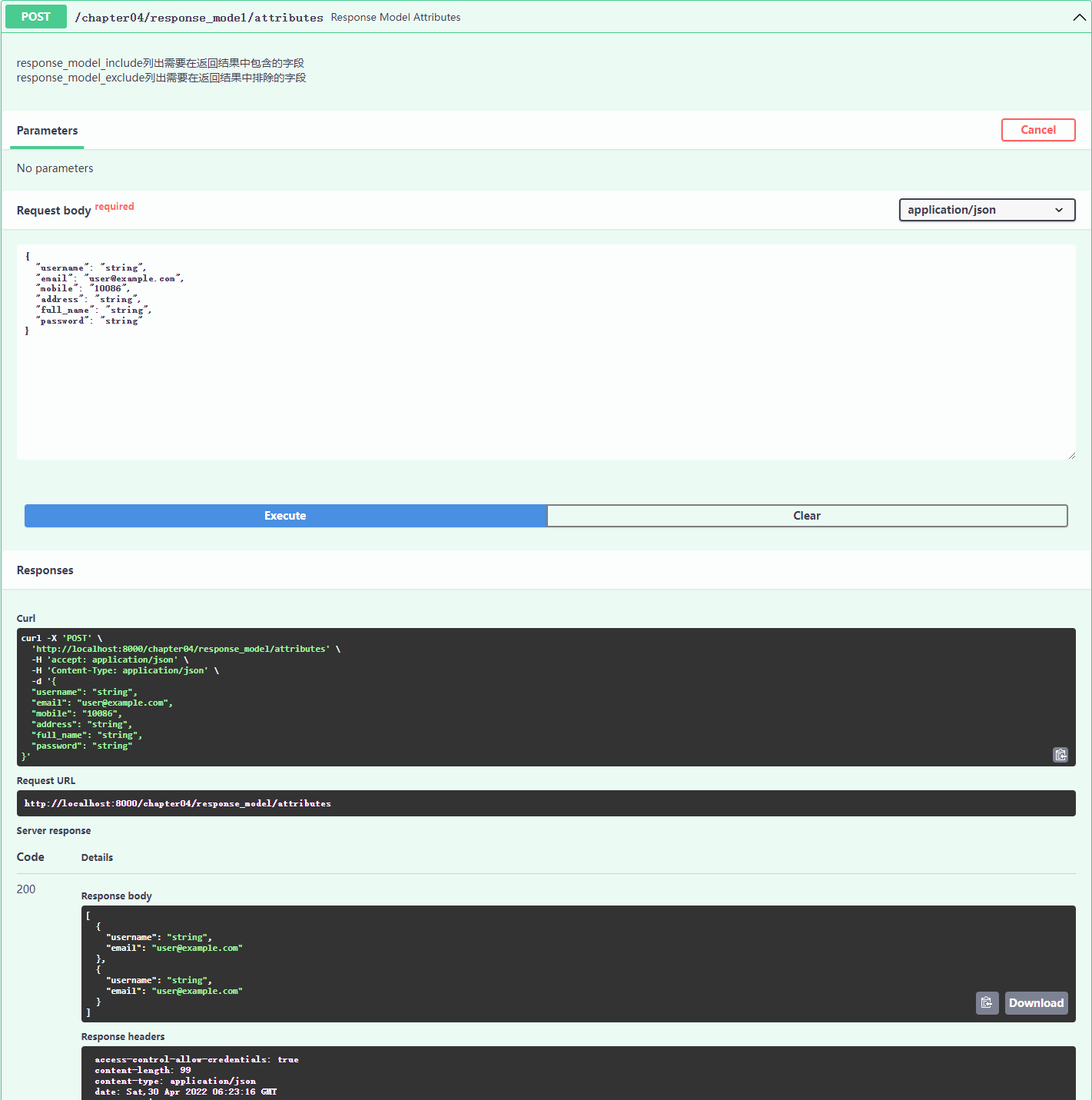
# 查询 page 页, 页大小为 pageSize 的员工信息
@router.get(
"/getStaffByPage/",
summary="分页按条目获取员工信息",
response_model= schema.StaffListGetResultModel,
response_model_exclude_unset=False,
)
async def get_staff_by_page(
page: int = 1,
pageSize: int = 10,
db:Session = Depends(get_db),
):
"""分页按条目获取员工信息
:param page: 页码
:param pageSize: 页大小
:param db: 数据库连接
:param response_model: 返回结果类型: schema.StaffListGetResultModel
:param response_model_exclude_unset: 是否排除未设置的字段, 表示默认值不包含在响应中, 仅包含实际给的值,
如果实际给的值与默认值相同也会包含在响应中
"""
staffs = crud.read_staff_by_page(db, page, pageSize)
return {
"result":{
"items":staffs,
"total": len(staffs)
},
}
响应状态码
在路由中通过 status_code 进行指定, 其值为整型, 可以通过 status.HTTP_xx_xx 获得名称上的提示
@app04.post("/status_code", status_code=200)
async def status_code():
"""返回status_code: 200"""
return {"status_code": 200}
@app04.post("/status_attribute", status_code=status.HTTP_200_OK)
async def status_attribute():
"""返回 status.HTTP_200_OK
"""
print(type(status.HTTP_200_OK))
return {"status_code": status.HTTP_200_OK}
表单数据处理
引入 fastapi.Form 用于处理表单数据
# from fastapi import Form # 用于处理表单数据
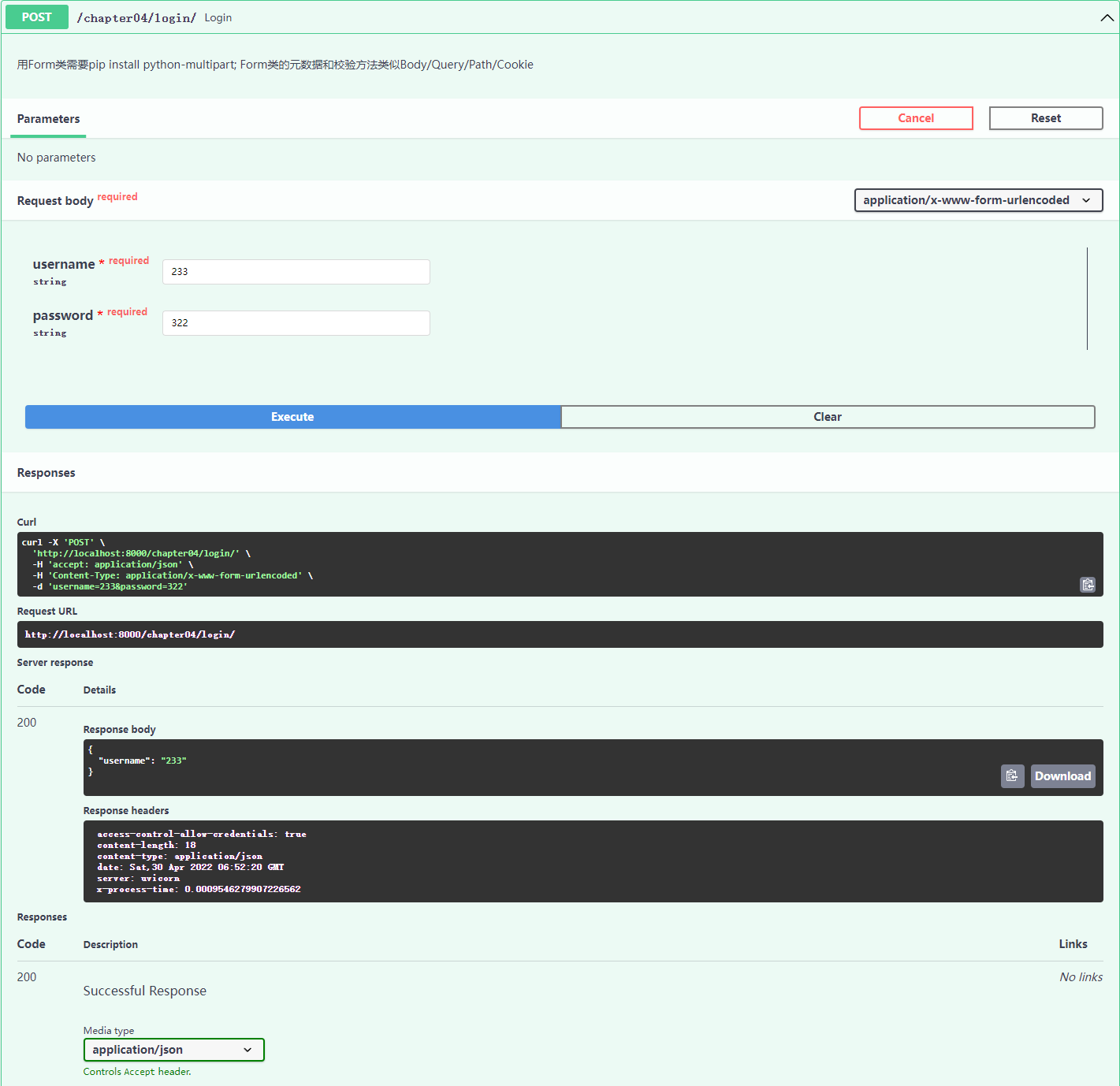
@app04.post("/login/")
async def login(username: str = Form(...), password: str = Form(...)): # 定义表单参数
"""
Form(...) 表示参数为必填项
用Form类需要pip install python-multipart;
Form类的元数据和校验方法类似Body/Query/Path/Cookie
"""
return {"username": username}
文件上传及参数详解
引入 fastapi.File & UploadFile, 路由函数参数中使用 File 和 UploadFile 来注解参数
"""Request Files 单文件、多文件上传及参数详解"""
# from fastapi import (
# File, # 文件处理
# UploadFile, # 用于处理文件上传
# )
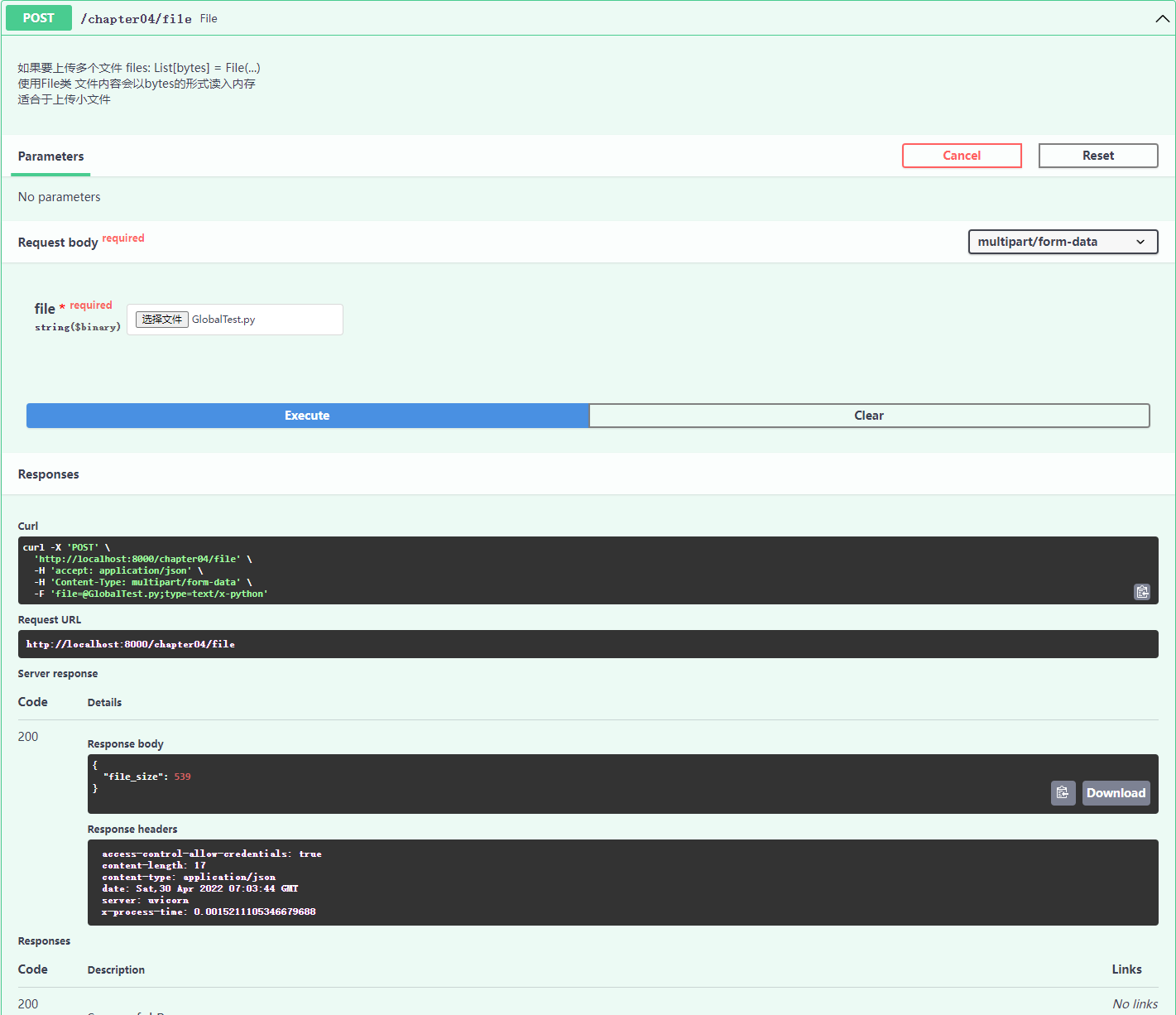
@app04.post("/file")
async def file_(file: bytes = File(...)):
"""
如果要上传多个文件 files: List[bytes] = File(...)
使用File类 文件内容会以bytes的形式读入内存
适合于上传小文件
"""
return {"file_size": len(file)}
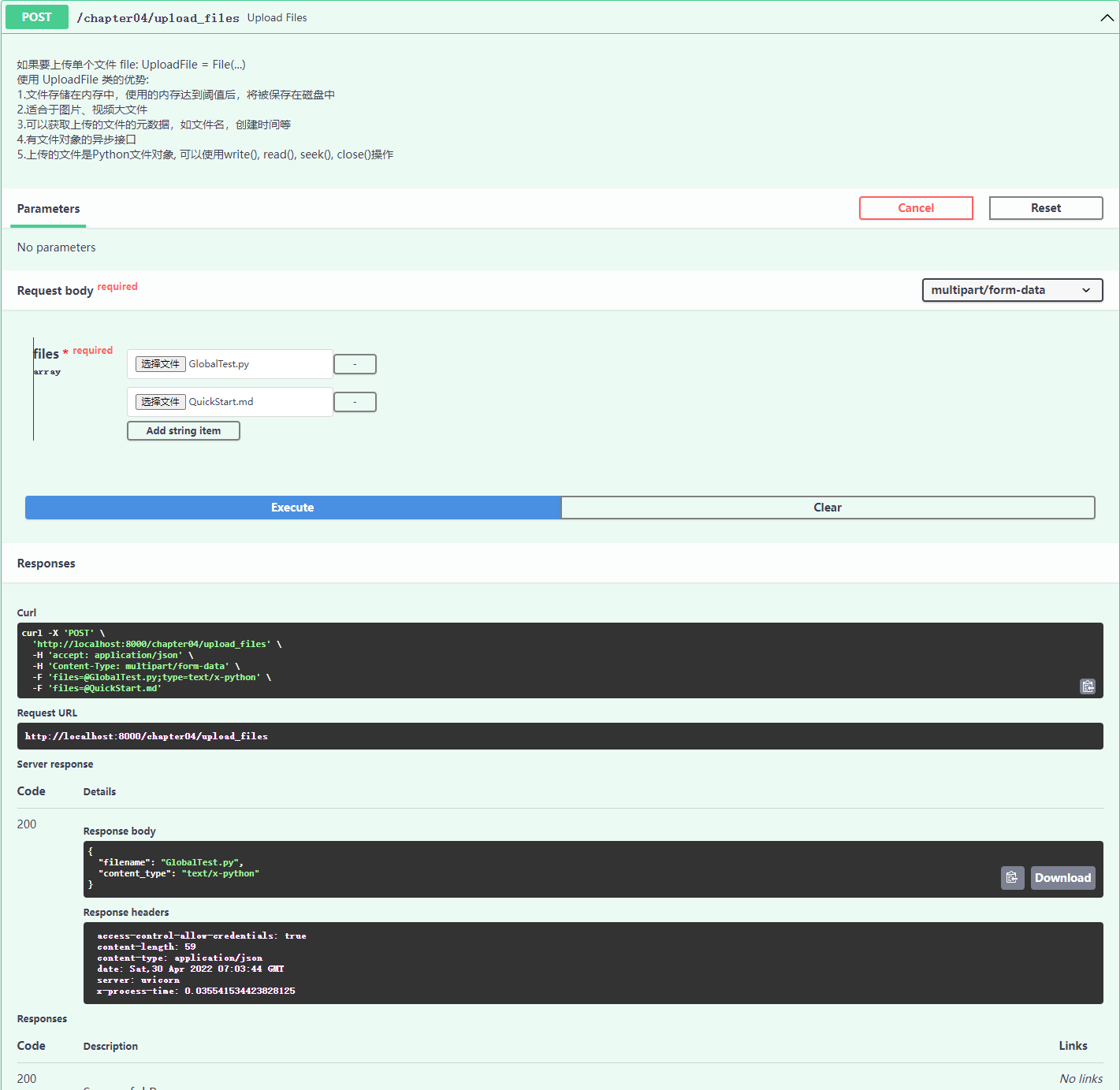
@app04.post("/upload_files")
async def upload_files(files: List[UploadFile] = File(...)):
"""
如果要上传单个文件 file: UploadFile = File(...)
使用 UploadFile 类的优势:
1.文件存储在内存中,使用的内存达到阈值后,将被保存在磁盘中
2.适合于图片、视频大文件
3.可以获取上传的文件的元数据,如文件名,创建时间等
4.有文件对象的异步接口
5.上传的文件是Python文件对象, 可以使用write(), read(), seek(), close()操作
"""
for file in files:
contents = await file.read()
print(contents)
return {"filename": files[0].filename, "content_type": files[0].content_type}
静态文件的配置
静态文件一般放在 static 文件夹中, 需要在 main app (而非 APIRouter 分路由) 中进行挂载方可使用
import os # 用于拼接路径
app = FastAPI(
title='FastAPI Tutorial and Coronavirus Tracker API Docs',
description='FastAPI教程 \
新冠病毒疫情跟踪器API接口文档, \
项目代码:https://github.com/liaogx/fastapi-tutorial',
version='1.0.0',
docs_url='/docs',
redoc_url='/redocs',
)
# mount表示将某个目录下一个完全独立的应用挂载过来,这个不会在API交互文档中显示
# .mount()不要在分路由APIRouter().mount()调用,模板会报错
static_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), './coronavirus/static'))
app.mount(path='/static', app=StaticFiles(directory=static_path), name='static')
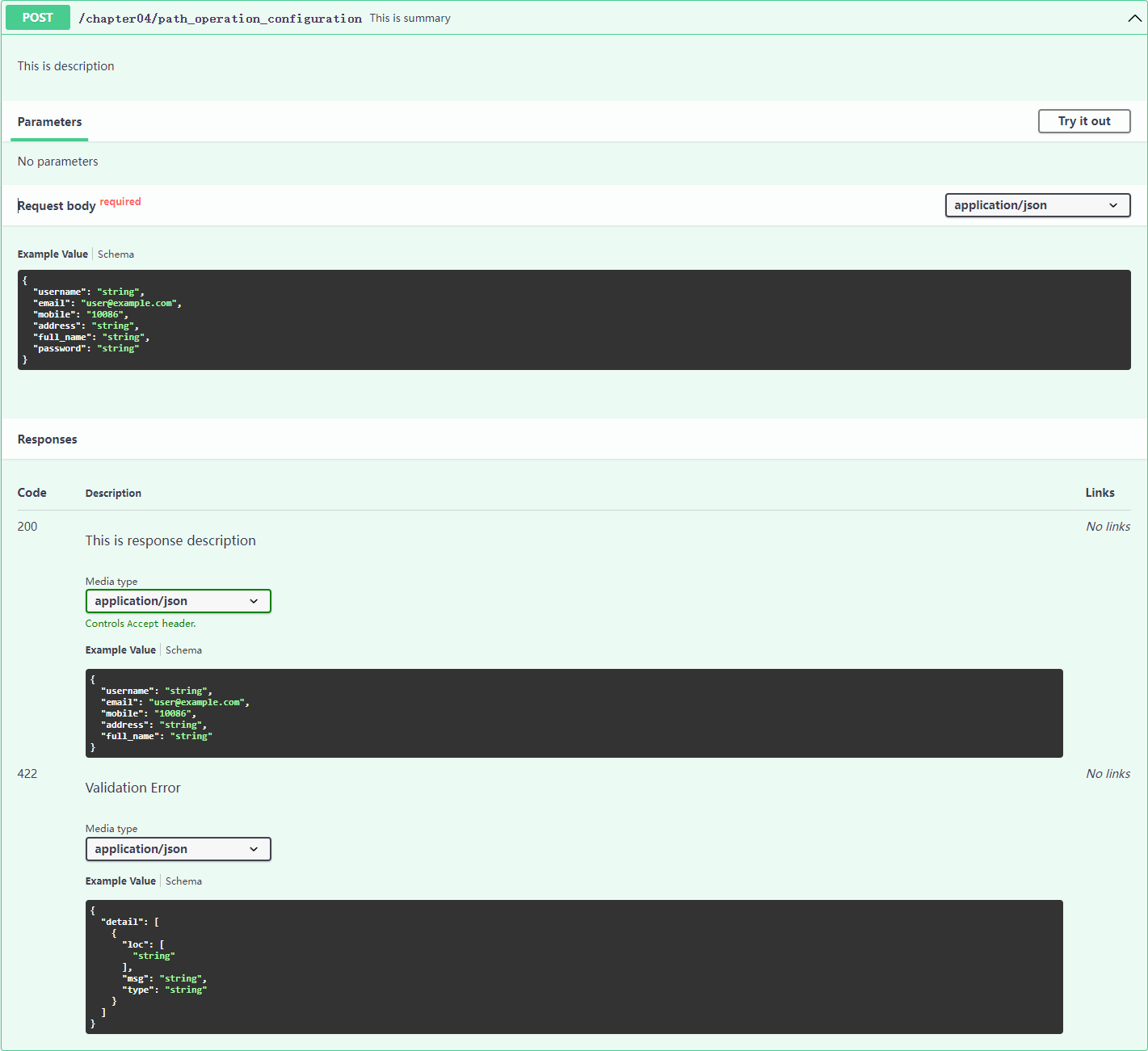
路径操作配置
"""Path Operation Configuration 路径操作配置"""
# 响应的状态码, 标签, 相应的描述符, 参数类型, 参数名称, 参数描述等等
@app04.post(
"/path_operation_configuration", # URL 地址
response_model=UserOut, # 响应的结果类型
# tags=["Path", "Operation", "Configuration"], # 标签, 在 doc 中会按照标签进行分类展示
summary="This is summary", # 接口描述, 在 doc 中会在路径后面显示
description="This is description", # 描述, 在 doc 中会在接口描述下面显示
response_description="This is response description", # 响应描述, 在 doc 中会在响应结果下面显示
# deprecated=True, # 是否弃用
status_code=status.HTTP_200_OK # 响应状态码
)
async def path_operation_configuration(user: UserIn):
"""
Path Operation Configuration 路径操作配置
:param user: 用户信息
:return: 返回结果
"""
return user.dict()
FastAPI 配置项
# FastAPI 配置项
app = FastAPI(
# 标题
title='FastAPI Tutorial and Coronavirus Tracker API Docs',
# 描述
description='FastAPI教程 \
新冠病毒疫情跟踪器API接口文档, \
项目代码:https://github.com/liaogx/fastapi-tutorial',
# 版本
version='1.0.0',
# Swagger UI 文档地址
docs_url='/docs',
# ReDoc 文档地址
redoc_url='/redocs',
)
错误处理
引入 fastapi.HTTPException 后在路由函数中进行使用
##### Handling Errors 错误处理 #####
# HTTP Exception 以及自定义异常处理器
# from fastapi import HTTPException # 用于处理HTTP异常
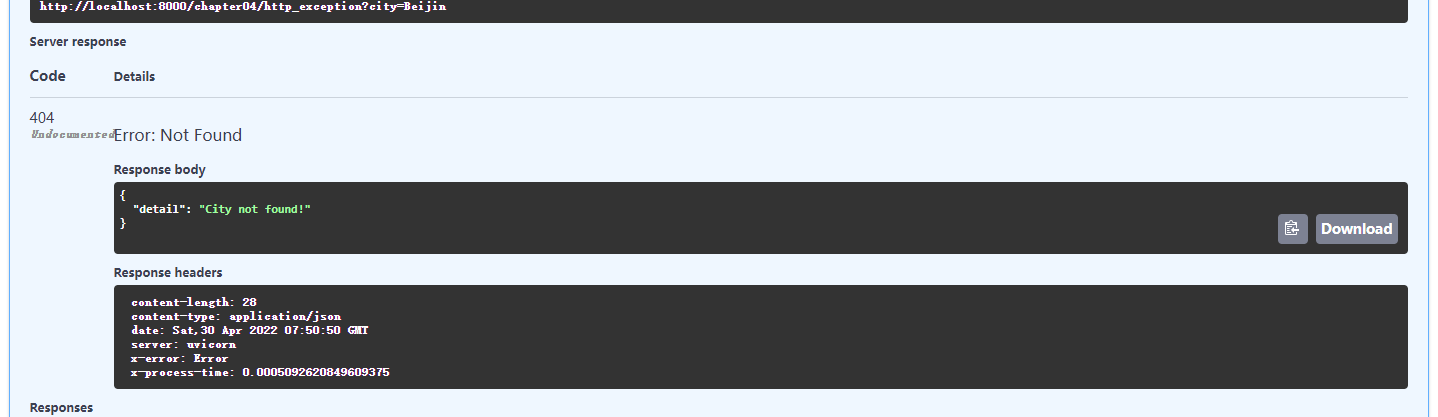
@app04.get("/http_exception")
async def http_exception(city: str):
"""默认的异常处理测试
:param city: 城市名称
:return: 返回城市名称
若 city 不是 Beijing 则抛出 404 错误
"""
if city != "Beijing":
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="City not found!", headers={"X-Error": "Error"})
return {"city": city}
自定义异常处理
在 main app 中进行异常处理的重写
from fastapi.exceptions import RequestValidationError # 请求校验错误处理
from fastapi.responses import PlainTextResponse # 文本形式返回 response
from starlette.exceptions import HTTPException as StarletteHTTPException # HTTP 异常处理
@app.exception_handler(StarletteHTTPException) # 重写HTTPException异常处理器
async def http_exception_handler(request, exc):
"""
使用文本形式返回异常信息
:param request: request 请求 (这个参数不能省)
:param exc: 错误
:return:
"""
return PlainTextResponse(str(exc.detail), status_code=exc.status_code)
#
#
@app.exception_handler(RequestValidationError) # 重写请求验证异常处理器
async def validation_exception_handler(request, exc):
"""
:param request: 这个参数不能省
:param exc:
:return:
"""
return PlainTextResponse(str(exc), status_code=400)
重写前HTTP异常:
重写后HTTP异常:
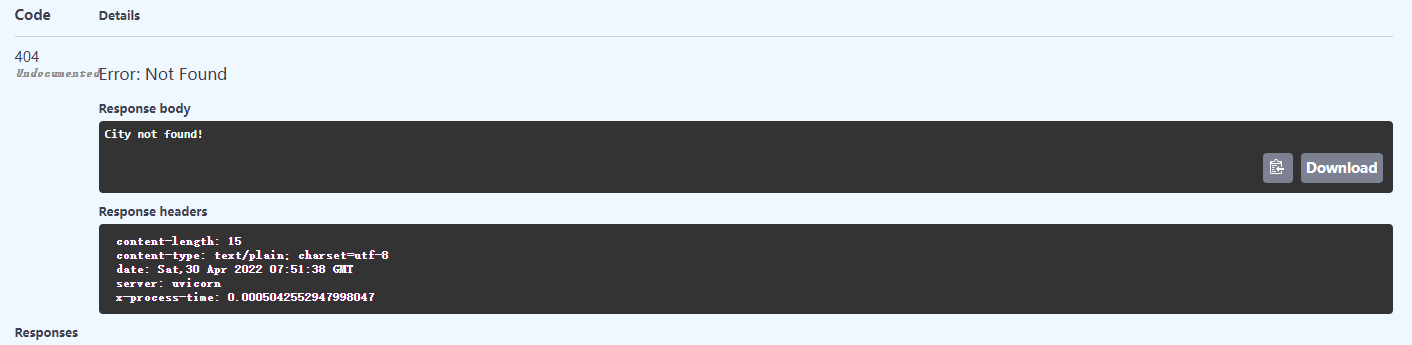
重写前请求异常:
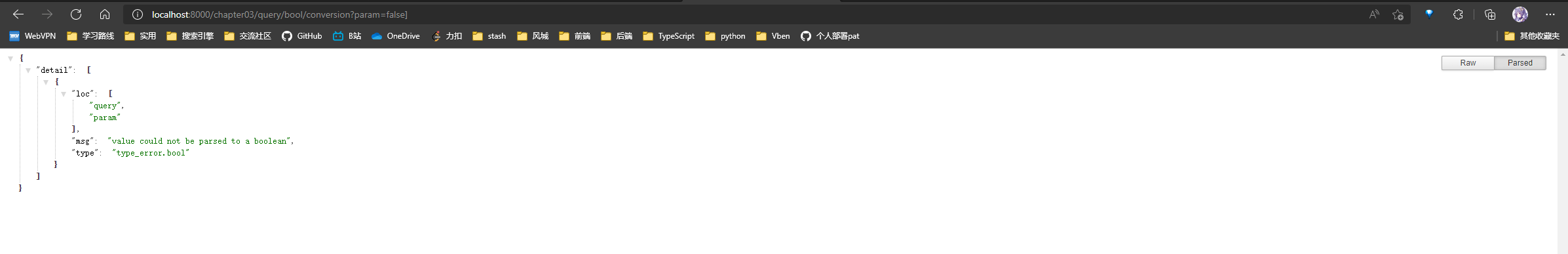
重写后请求异常: